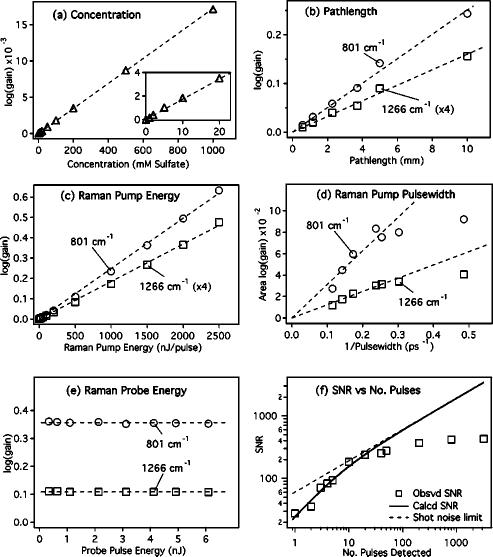
FIG. 4.
Dependence of the stimulated Raman gain intensity on experimental parameters. The Raman gain of the 981 cm–1 sulfate peak increases exponentially with concentration (a). The intensities of the 801 and 1266 cm–1 peaks of cyclohexane increase exponentially with changes in pathlength (b), Raman pump pulse energy (c), and 1/pump pulse duration [FWHM–1 (d)]. In (e), the gain is shown to be independent of Raman probe energy. The observed SNR (f) for the 1266 cm–1 peak of cyclohexane follows the theoretical limit for exposures of ∼20 pulses. With longer exposures, the systematic noise of the detector limits the SNR.