Figure 3.
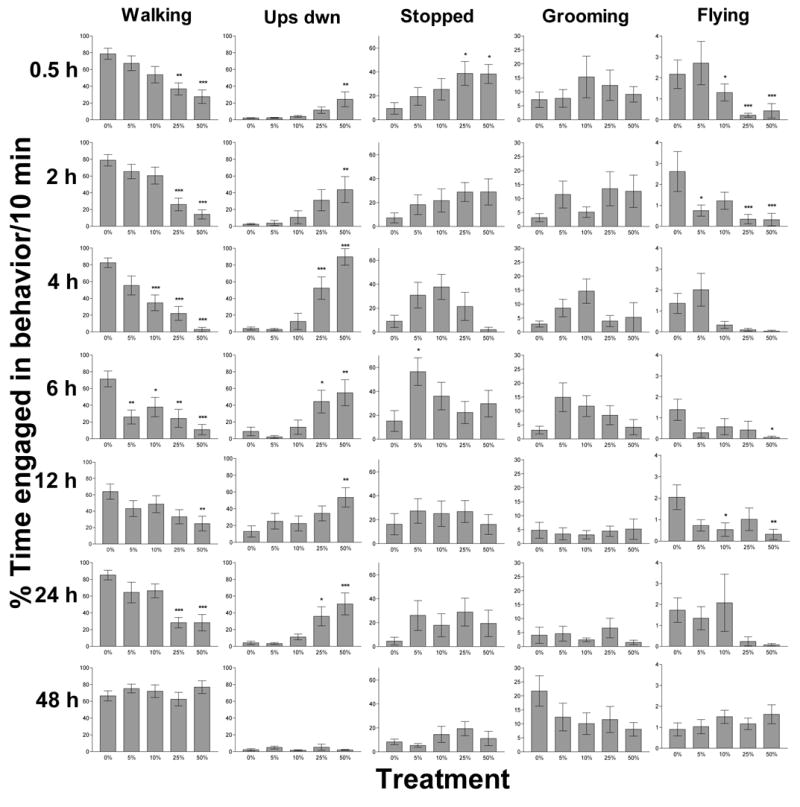
Recovery time from ethanol inebriation was dose-dependent (P < 0.001) and occurred for all treatments by 48 h post-ingestion. To assess recovery, we compared time spent walking for subjects in each ethanol treatment to the control group (0%). Although the amount of time engaged in walking is slightly lower than that for control, subjects given 5 or 10% ethanol appear to recover between 12–24 h after ethanol ingestion. In contrast, the subjects that ingested 25 or 50% ethanol required 24 to 48 h to recover. Asterisks (*) indicate significant P-values for Dunnett’s multiple comparisons of each ethanol treatment against the control (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001). Bars represent the mean time subjects spent in the indicated behavior +/− SEM. N = 10 per treatment for the 0.5, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h time points and N = 15 per treatment for the 12 and 48 h time points.
