Abstract
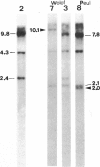
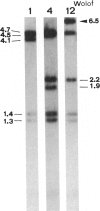
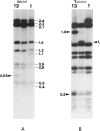
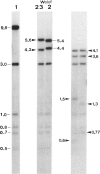
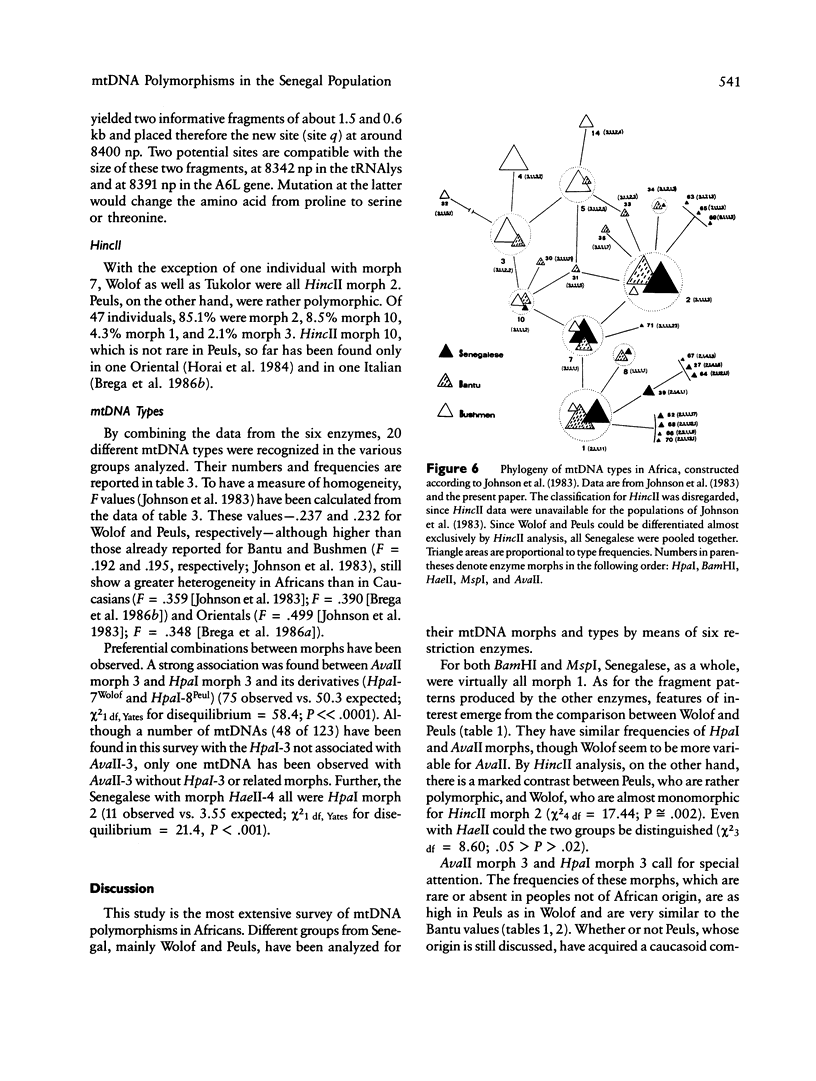
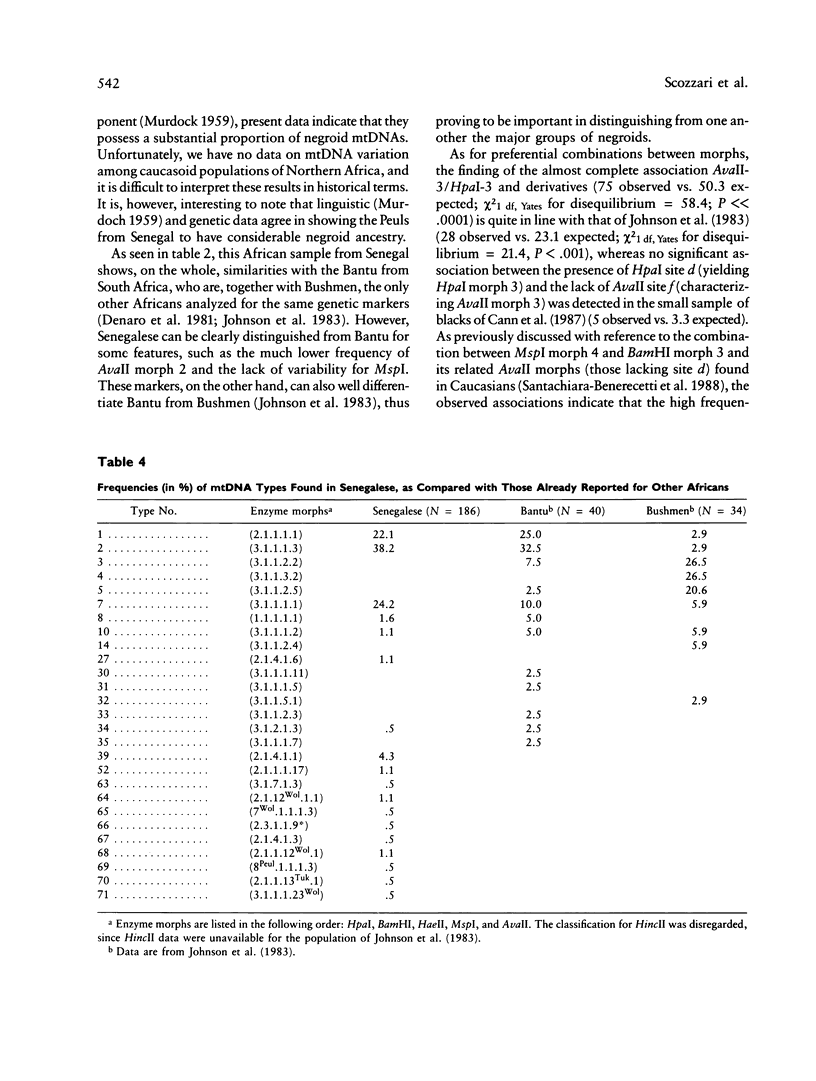
The mtDNA of 186 Senegalese, mainly Wolof and Peuls, were analyzed by means of six restriction enzymes: HpaI, BamHI, HaeII, MspI, AvaII, and HincII. Two of the HpaI, one of the HaeII, two of the MspI, and one of the AvaII morphs had not been described before. The only enzymes which enabled Wolof and Peuls to be differentiated were HincII and, to a lesser extent, HaeII. Important differences emerge in the comparison of Senegalese with Bantu of South Africa and with Bushmen, the only other Africans who, as far as we know, were studied for the same genetic markers. Though Senegalese mtDNAs display typical African features (presence and frequency of HpaI morph 3 and high incidence of AvaII morph 3), the distribution of MspI and AvaII patterns markedly differentiates Senegalese from the others. The phylogeny of mtDNA types in Africa well portrays how the three African groups are clearly distinguishable genetic entities. Bushmen lie at one end of the range of variability, Senegalese being at the other end but still fairly closely related to Bantu. The information provided by individual restriction enzymes to the distinction among the three major ethnic groups is reviewed and discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanc H., Chen K. H., D'Amore M. A., Wallace D. C. Amino acid change associated with the major polymorphic Hinc II site of Oriental and Caucasian mitochondrial DNAs. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Mar;35(2):167–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonné-Tamir B., Johnson M. J., Natali A., Wallace D. C., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Human mitochondrial DNA types in two Israeli populations--a comparative study at the DNA level. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;38(3):341–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brega A., Gardella R., Semino O., Morpurgo G., Astaldi Ricotti G. B., Wallace D. C., Santachiara Benerecetti A. S. Genetic studies on the Tharu population of Nepal: restriction endonuclease polymorphisms of mitochondrial DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):502–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brega A., Scozzari R., Maccioni L., Iodice C., Wallace D. C., Bianco I., Cao A., Santachiara Benerecetti A. S. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms in Italy. I. Population data from Sardinia and Rome. Ann Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;50(Pt 4):327–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1986.tb01754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M. Polymorphism in mitochondrial DNA of humans as revealed by restriction endonuclease analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3605–3609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Brown W. M., Wilson A. C. Polymorphic sites and the mechanism of evolution in human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics. 1984 Mar;106(3):479–499. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):31–36. doi: 10.1038/325031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics. 1983 Aug;104(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denaro M., Blanc H., Johnson M. J., Chen K. H., Wilmsen E., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Wallace D. C. Ethnic variation in Hpa 1 endonuclease cleavage patterns of human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5768–5772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles R. E., Stroynowski I., Wallace D. C. Characterization of mitochondrial DNA in chloramphenicol-resistant interspecific hybrids and a cybrid. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Jul;6(4):543–554. doi: 10.1007/BF01539155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harihara S., Hirai M., Omoto K. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Japanese living in Hokkaido. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1986 Jun;31(2):73–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01871401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Gojobori T., Matsunaga E. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Japanese. I. Analysis with restriction enzymes of six base pair recognition. Hum Genet. 1984;68(4):324–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00292594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai S., Matsunaga E. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in Japanese. II. Analysis with restriction enzymes of four or five base pair recognition. Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;72(2):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00283927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. J., Wallace D. C., Ferris S. D., Rattazzi M. C., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Radiation of human mitochondria DNA types analyzed by restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(3-4):255–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M. Evolution of human races at the gene level. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;103(Pt A):167–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santachiara Benerecetti A. S., Scozzari R., Semino O., Torroni A., Brega A., Wallace D. C. Mitochondrial DNA polymorphisms in Italy. II. Molecular analysis of new and rare morphs from Sardinia and Rome. Ann Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;52(Pt 1):39–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1988.tb01076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Garrison K., Knowler W. C. Dramatic founder effects in Amerindian mitochondrial DNAs. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1985 Oct;68(2):149–155. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330680202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Surti U., Adams C. W., Szulman A. E. Complete moles have paternal chromosomes but maternal mitochondrial DNA. Hum Genet. 1982;61(2):145–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00274205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]