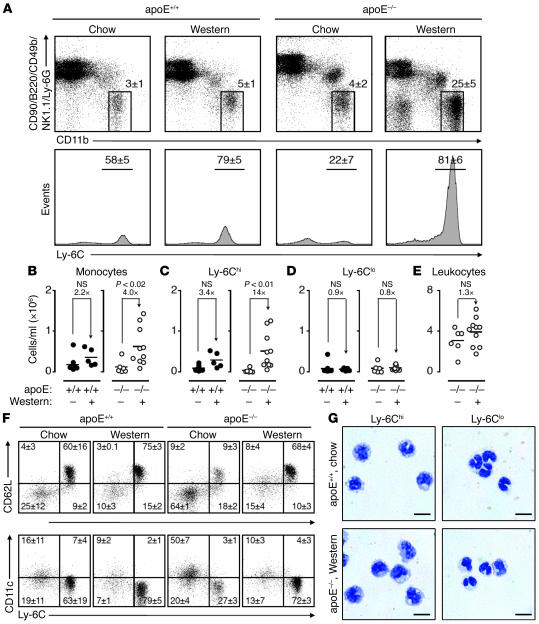
Figure 1. Hypercholesterolemia induces peripheral blood Ly-6Chi monocytosis.
(A) Mononuclear cells from blood of apoE+/+ and apoE–/– mice consuming either chow or Western diet were stained with anti-CD11b, -CD90, -B220, -CD49b, -NK1.1, –Ly-6G, and –Ly-6C mAbs. Living cells were gated to determine presence and percentage of CD11bhiCD90loB220loCD49bloNK1.1loLy-6Glo monocytes (top row) and further divided into Ly-6Chi and Ly-6Clo subsets (bottom row). Representative dot plots and histograms from individual mice are depicted. Percentages of cells are shown as mean ± SEM. (B) Total blood monocytes in apoE+/+ and apoE–/– mice consuming either Western diet (+) or chow (–). (C) Total blood Ly-6Chi monocytes. (D) Total blood Ly-6Clo monocytes. (E) Total peripheral blood leukocytes. (F) Representative dot plots depicting expression of CD62L and CD11c among Ly-6Chi and Ly-6Clo monocytes. Percentages of cells in each quadrant are shown as mean ± SEM. (G) Representative cytospin preparations of purified blood Ly-6Chi and Ly-6Clo monocytes in apoE+/+ mice on chow and apoE–/– mice on Western diet. Scale bar: 10 μm. Student’s t test was used. Results are representative of 8 independent experiments with 5–14 mice per group.