Abstract
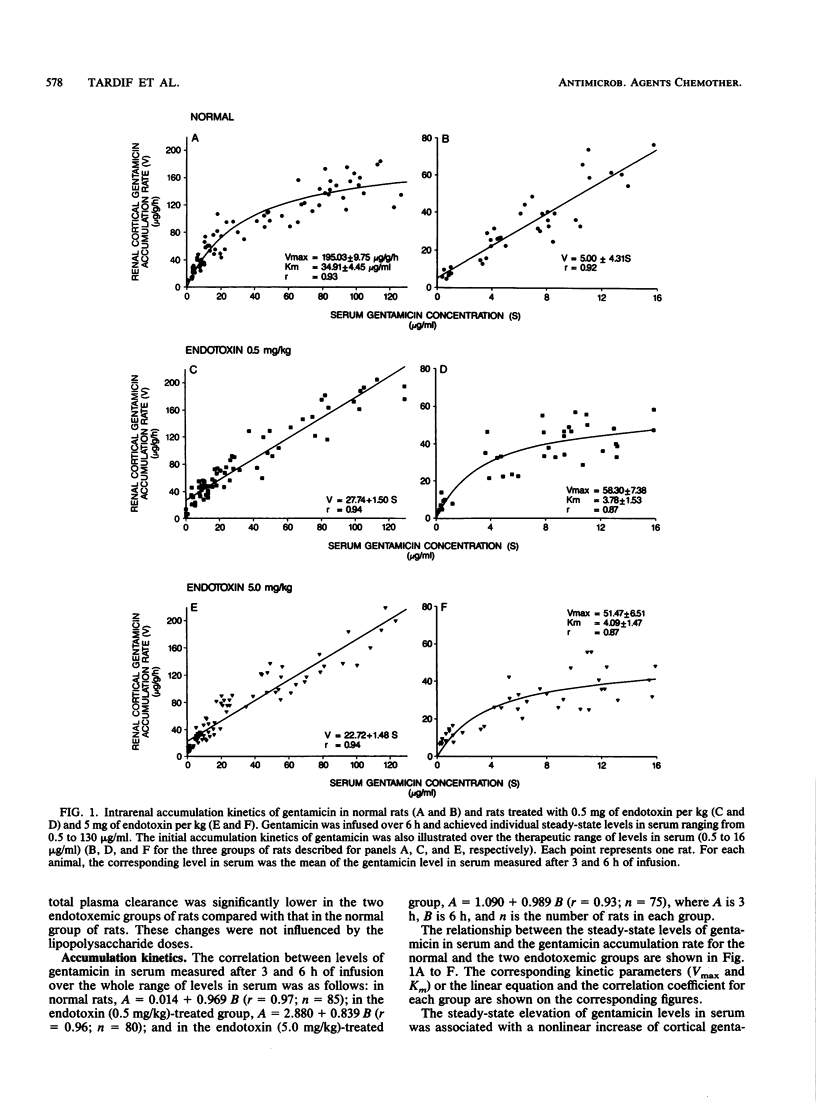
The mechanism by which endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) modifies the intrarenal distribution and the nephrotoxic potential of gentamicin is unknown. We studied the influence of LPS on the intracortical accumulation kinetics of gentamicin in rats infused intravenously for 6 h, during which time steady-state levels of the antibiotic in serum were achieved. We compared gentamicin accumulation rates (V) in normal rats and in rats receiving LPS (0.5 and 5 mg/kg) as levels in serum (S) varied from 0.5 to 130 micrograms/ml. The pharmacokinetic parameters of gentamicin were previously measured in the three groups of rats that were studied in order to reach and maintain in each rat the desired levels of antibiotic in serum during the 6 h of infusion. Two hours before the infusion of gentamicin, LPS was injected intravenously over a period of 15 min. In normal rats, the increase in S was associated with a nonlinear increase in V. The Michaelis-Menten kinetics, which was the best-fitting function, gave an apparent Vmax (maximal capacity of uptake) of 195.03 +/- 9.75 micrograms/g per h and an apparent Km (concentration in serum at Vmax/2, an index of affinity) of 34.91 +/- 4.45 micrograms/ml (linear transformation of the experimental data by the Hanes-Woolf plot: r = 0.93, n = 85). In the rats that received LPS, the increase in S was associated with a linear increase of V: for LPS at 0.5 mg/kg, V = 27.00 + 1.50 S (r = 0.94, n = 80); for LPS at 5 mg/kg, V = 22.72 + 1.48 S (r = 0.94, n = 75). We conclude that endotoxin modifies the accumulation kinetics of gentamicin in the kidney cortices of rats.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Murray T., Hamburger R. J. Uptake of gentamicin by separated, viable renal tubules from rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):510–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y. Influence of endotoxin on the intrarenal distribution of gentamicin, netilmicin, tobramycin, amikacin, and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y., Marois Y. Autoradiography of tobramycin uptake by the proximal and distal tubules of normal and endotoxin-treated rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1005–1009. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Trottier S. Influence of single or multiple doses of gentamicin and netilmicin on their cortical, medullary, and papillary distribution. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):635–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bacterial endotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:67–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier V. U., Lietman P. S., Mitch W. E. Evidence for luminal uptake of gentamicin in the perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Aug;210(2):247–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT R. P. Mechanisms of the hemodynamic effects of endotoxin. Physiol Rev. 1960 Apr;40:245–279. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano R. A., Verpooten G. A., Verbist L., Wedeen R. P., De Broe M. E. In vivo uptake kinetics of aminoglycosides in the kidney cortex of rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkin H., Lidji M., Rubinstein E. The influence of endotoxin-induced pyrexia on the pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Feb;216(2):415–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josepovitz C., Pastoriza-Munoz E., Timmerman D., Scott M., Feldman S., Kaloyanides G. J. Inhibition of gentamicin uptake in rat renal cortex in vivo by aminoglycosides and organic polycations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Erdmann G., Habermann E. The renal handling of polybasic drugs. 1. Gentamicin and aprotinin in intact animals. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00505080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluwe W. M., Hook J. B. Analysis of gentamicin uptake by rat renal cortical slices. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;45(2):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90115-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Carlier M. B., Rollman B., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P. Mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis: in vitro and in vivo studies with gentamicin and amikacin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3861–3870. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky J. J., Cheng L., Sacktor B., Lietman P. S. Gentamicin uptake by renal tubule brush border membrane vesicles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Nov;215(2):390–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manny J., Livni N., Schiller M., Guttman A., Boss J., Rabinovici N. Structural changes in the perfused canine kidney exposed to the direct action of endotoxin. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Mar;16(3):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastrasinh M., Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Identification of the aminoglycoside binding site in rat renal brush border membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr Affinity of endotoxin for membranes. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):197–201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Mogan K. A. Kinetics of endotoxin release during antibiotic therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):380–388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. The physiological disturbances produced by endotoxins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1954;16:467–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.16.030154.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber D. L., Adair T. H., Adams T., Jr Hemodynamic consequences of endotoxemia in sheep. Circ Shock. 1981;8(5):551–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Cachectin: a hormone that triggers acute shock and chronic cachexia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):413–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trnovec T., Bezek S., Kállay Z., Durisová M., Navarová J. Non-linear accumulation of gentamicin in guinea-pig kidney. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Nov;14(5):543–548. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen R. P., Batuman V., Cheeks C., Marquet E., Sobel H. Transport of gentamicin in rat proximal tubule. Lab Invest. 1983 Feb;48(2):212–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenfelder M., Galanos C., Madsen P. O. Experimental lipid A-induced nephritis in the dog. Invest Urol. 1975 Mar;12(5):337–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. C., Goetsch D. D., Huber T. L. Influence of endotoxin-induced fever on the pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in ewes. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2495–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. C., Moore J. N., Eakle N. Gentamicin pharmacokinetics in horses given small doses of Escherichia coli endotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Sep;44(9):1746–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


