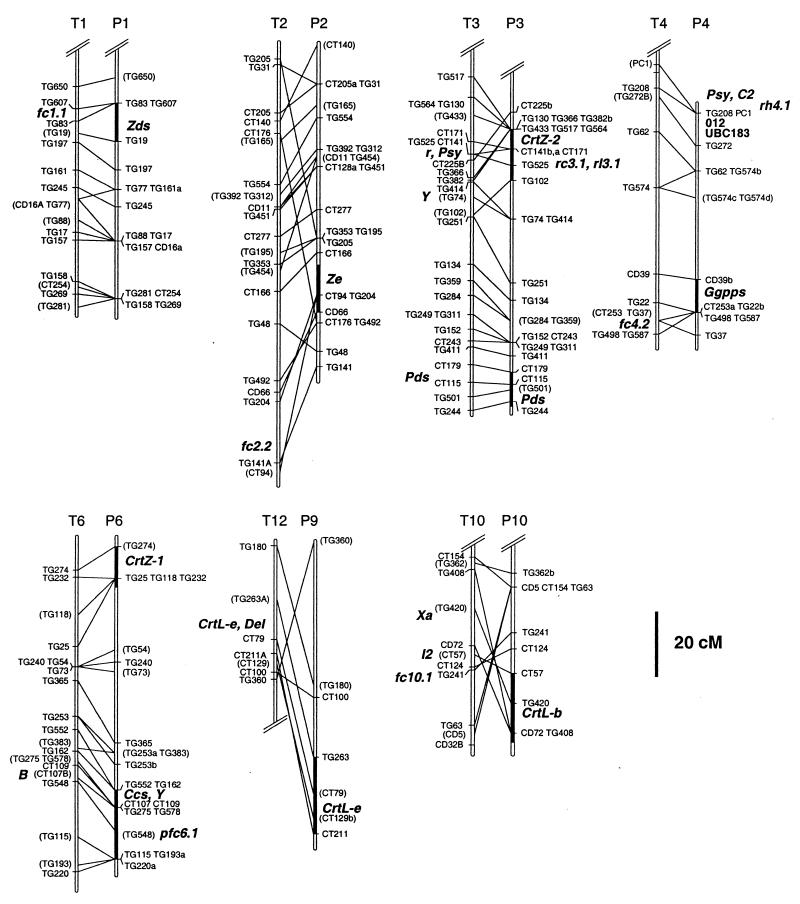
Figure 2.
Comparative map of pepper and tomato chromosomes, showing the position of carotenoid structural genes and phenotypically defined loci. T1, T2, T3, T4, T6, T10, and T12 refer to tomato chromosomes from ref. 57. P1, P2, P3, P4, P6, P9, and P10 refer to pepper chromosomes defined in ref. 38. Double slash marks at termini indicate that partial chromosomes are shown. Markers consist of tomato genomic (TG) and tomato cDNA (CD and CT) clones. Maps were aligned according to ref. 38, and lines between chromosomes connect presumed orthologues. Pepper genes are geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase (Ggpps), phytoene synthase (Psy), phytoene desaturase (Pds), ζ-carotene desaturase (Zds), lycopene β-cyclase (CrtL-b), lycopene ɛ-cyclase (CrtL-e), β-carotene hydroxylase-1 and -2 (CrtZ-1 and -2), zeaxanthin epoxidase (Ze), and capsanthin–capsorubin synthase (Ccs). The darkened chromosomal segment associated with each of the carotenoid genes indicates the support interval for each gene, including all positions with ΔLOD ≤ 2. O-12 and UBC183 are RAPDs linked to C2. Pepper QTL are pfc6.1, rc3.1, rl3.1, and rh4.1 (50, 55). Tomato genes are Psy, Pds, and CrtL-e. Tomato mutants are lutescent-2 (l2), Xa, Delta (Del), yellow-flesh (r), and B. Tomato map positions are from refs. 30, 31, 56, and 57. Tomato QTL (fc2.2, fc4.2, fc10.1) are from ref. 32 and fc1.1 is from ref. 33. The Y locus of potato shown on T3 was mapped in ref. 47. Placement of the locus designation reflects the best inferred position for the locus on this map.