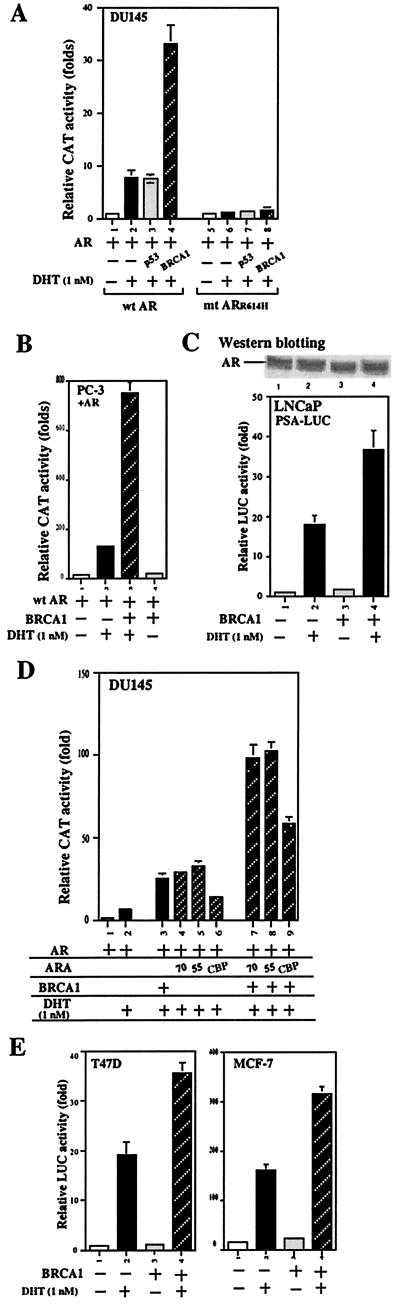
Figure 1.
Potentiation of the AR transactivation by BRCA1. (A) BRCA1, but not p53, potentiates the wild-type AR transactivation in prostate cancer cells. In each 60-mm dish of DU145 cells, 1 μg of pSG5-AR, 3 μg of MMTV-CAT, and/or 4.5 μg of pCR3-BRCA1, or 4.5 μg of p53 were transfected into cells by calcium phosphate method (14). The total plasmid amount was adjusted with pSG5, pCR3, or pCMV parent vector to 11 μg for each 60-mm transfection by calcium phosphate precipitation method. (B) BRCA1 can potentiate the AR transactivation in PC-3 cell. Cells were transfected as mentioned above. (C) BRCA1 can potentiate the AR transactivation in LNCaP cells in the presence of androgen without changing the expression of AR. 0.5 μg of PSA-LUC and 1.0 μg of pCR3 or pCR3-BRCA1 were transfected into LNCaP cells in 35-mm dish for 2 h by SuperFect. Cells were then treated with 1 nM DHT for an additional 24 h and harvested for LUC assay. The relative LUC activity was normalized against Renilla LUC activity (Promega). Data represent an average of three independent experiments. Duplicate LNCaP cells were harvested, and 60 μg of whole-cell extract was assayed with Western blotting for the detection of AR protein. The ectopically expressed BRCA1 cannot affect the expression of endogenous AR in LNCaP cells. (D) AR coregulators could cooperate with BRCA1 to synergistically enhance the AR transactivation. DU145 cells were cotransfected with 3 μg of MMTV-CAT, 1 μg of pSG5-AR, and 3 μg of alone or together with 3 μg CBP, ARA70N, ARA55, or BRCA1, in the absence or presence of 1 nM DHT. The error bars represent the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. (E) BRCA1 can potentiate the AR transactivation in MCF-7 and T47D cells. 0.5 μg of PSA-LUC reporter plasmid or 1.0 μg of pCR3-BRCA1 were transfected into T47D and MCF-7 cells. Cells were treated with 1 nM DHT after transfection as mentioned above.