Figure 2.
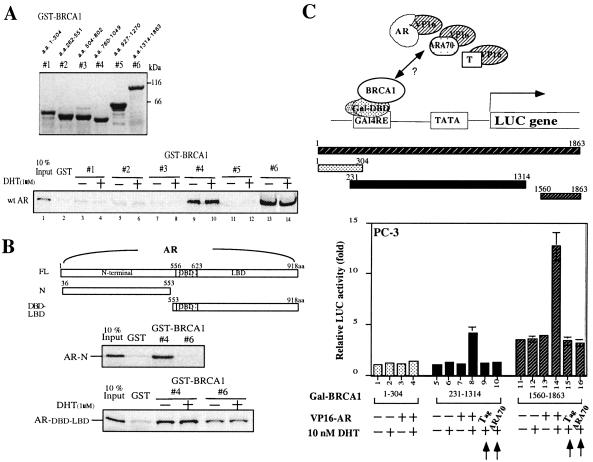
The interaction between BRCA1 and AR. (A) Mapping the domains of BRCA1 that are responsible for AR interaction. Six recombinant GST–BRCA1 fusion proteins, fragments #1, #2, #3, #4, #5, and #6, were generated in Escherichia coli as described. BRCA1 residues are marked relative to the translation initiation site. The Coomassie blue-stained SDS polyacrylamide gel, showing the relative abundance of each fusion protein, was used in the GST pull-down assay as described. The 110-kDa protein bound to GST–BRCA1 #4 and #6 is a product of 35S-methionine-labeled full-length AR. (B) Mapping the domain of AR that is required for BRCA1 interaction. 20 μl of in vitro translated 35S-methionine-labeled AR N (from amino acids 36–553) and AR DBD-LBD (from amino acids 553–918) protein was used to perform the pull-down assay. The results indicated that GST–BRCA1 fragment #4 (amino acids 758-1064) can interact both with the N-terminal and DBD-LBD of AR. In contrast, GST–BRCA1 #6 (amino acids 1314–1863) can associate with only the DBD- LBD of AR. Our data indicate that there are two contact pockets between BRCA1 and AR. (C) The interaction between AR and BRCA1 by mammalian two-hybrid assay. PC-3 cells in 35-mm dishes were transiently cotransfected with 0.5 μg of reporter plasmid pG5-LUC, and 0.75 μg of Gal4DBD fused BRCA1 constructs, amino acids 1–304, amino acids 231-1314, amino acids 1560–1863, with or without 0.75 μg of VP16 fused AR (VP16-AR) construct for 2 h by SuperFect. 1 nM DHT was added for another 24 h, and then the cells were harvested for LUC assay. Arrows indicate VP16-fused SV40 large T antigen and ARA70 were applied here to assure the interaction specificity between BRCA1 and AR. The results indicate that BRCA1 amino acids 231-1314 and amino acids 1560–1863 are responsible for AR interaction; these results are consistent with the results from GST pull-down assay.