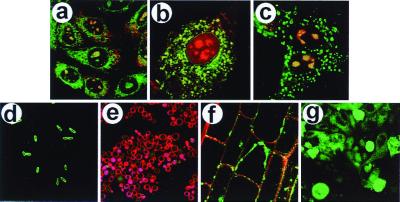
Figure 2.
Delivery of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD into eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. All images shown were recorded at 10 min after addition of the carrier-cargo complex. (a) The uptake of complexes of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD and Neo-RB by CHO cells. (b) Uptake of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD-Neo-XRITC complexes by a 3T3-L1 preadipocyte. (c) Uptake of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD-Neo-RB complexes by MDCK cells. (d) Uptake of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD (histone carrier) by E. coli cells. (e) Uptake of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD (histone carrier) by S. cerevisiae cells. The red fluorescence in the plasma membrane is a result of FM 4–64 staining after analog delivery. (f) Uptake of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD-Neo-RB complexes by A. thaliana root-tip cells. (g) Uptake of PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD (histone carrier) by C. parvum cells on a field of epithelial cells (background). For each image, the green fluorescence is caused by the PtdIns(4,5)P2-NBD, the red fluorescence is emitted by either Neo-RB or Neo-XRITC (except e), and the yellow regions are caused by colocalization of red and green fluorophores. Magnifications: a, ×260; b and d, ×600; c, ×400; e and g, ×160; and f, ×480.