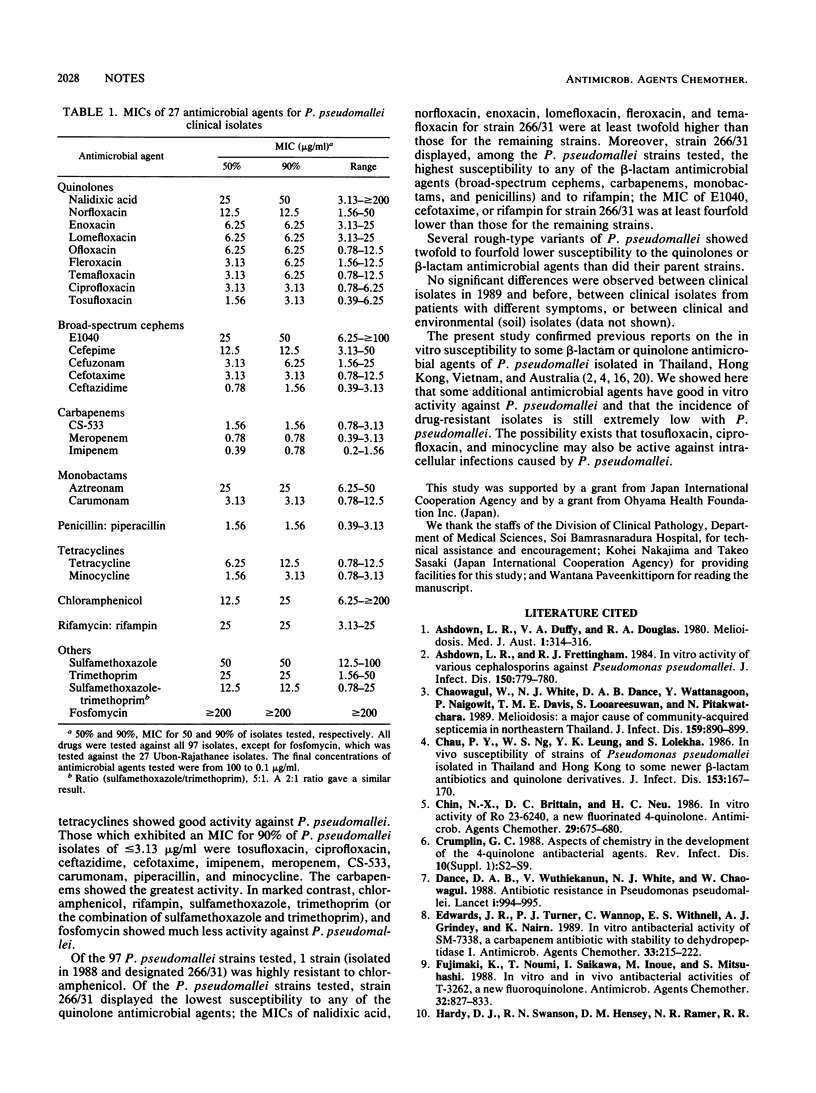
Abstract
Clinical isolates of Pseudomonas pseudomallei isolated in Thailand from 1981 to 1989 were tested for their in vitro susceptibilities to 27 antimicrobial agents, including older and newer quinolones, broad-spectrum cephems, carbapenems, monobactams, penicillins, tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, rifamycin, sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, and fosfomycin. Tosufloxacin, meropenem, CS-533, and minocycline were active against P. pseudomallei at levels comparable to or even greater than those of antimicrobial agents tested in previous studies, such as ciprofloxacin, ceftazidime, imipenem, carumonam, and piperacillin. Drug-resistant P. pseudomallei was found in only 1% of the isolates. The drug-resistant P. pseudomallei isolates displayed a unique pattern of susceptibility to the above-listed drugs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashdown L. R., Duffy V. A., Douglas R. A. Meliodosis. Med J Aust. 1980 Apr 5;1(7):314–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashdown L. R., Frettingham R. J. In vitro activity of various cephalosporins against Pseudomonas pseudomallei. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):779–780. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaowagul W., White N. J., Dance D. A., Wattanagoon Y., Naigowit P., Davis T. M., Looareesuwan S., Pitakwatchara N. Melioidosis: a major cause of community-acquired septicemia in northeastern Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):890–899. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Ng W. S., Leung Y. K., Lolekha S. In vitro susceptibility of strains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei isolated in Thailand and Hong Kong to some newer beta-lactam antibiotics and quinolone derivatives. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):167–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C. Aspects of chemistry in the development of the 4-quinolone antibacterial agents. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10 (Suppl 1):S2–S9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dance D. A., Wuthiekanun V., White N. J., Chaowagul W. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):994–995. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91810-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. R., Turner P. J., Wannop C., Withnell E. S., Grindey A. J., Nairn K. In vitro antibacterial activity of SM-7338, a carbapenem antibiotic with stability to dehydropeptidase I. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):215–222. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimaki K., Noumi T., Saikawa I., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of T-3262, a new fluoroquinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):827–833. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Swanson R. N., Hensey D. M., Ramer N. R., Bower R. R., Hanson C. W., Chu D. T., Fernandes P. B. Comparative antibacterial activities of temafloxacin hydrochloride (A-62254) and two reference fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1768–1774. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Sampath A., Spotnitz M. The pseudomallei group: a review. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):598–606. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai K., Dejsirilert S. Pseudomonas pseudomallei and melioidosis, with special reference to the status in Thailand. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1988 Aug;41(4):123–157. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.41.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Bies M., Buck R. E., Chisholm D. R., Pursiano T. A., Tsai Y. H., Misiek M., Price K. E., Leitner F. Comparison of a new cephalosporin, BMY 28142, with other broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEniry D. W., Gillespie S. H., Felmingham D. Susceptibility of Pseudomonas pseudomallei to new beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21(2):171–175. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Saha G., Labthavikul P. In vitro activity against aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and beta-lactamase stability of RS-533, a novel carbapenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):828–834. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Katsu K., Moriyama M., Kitoh K. In vitro evaluation of E1040, a new cephalosporin with potent antipseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):693–701. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winton M. D., Everett E. D., Dolan S. A. Activities of five new fluoroquinolones against Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):928–929. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Matthews R. S. In vitro activity of lomefloxacin, a new quinolone antimicrobial agent, in comparison with those of other agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):617–622. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


