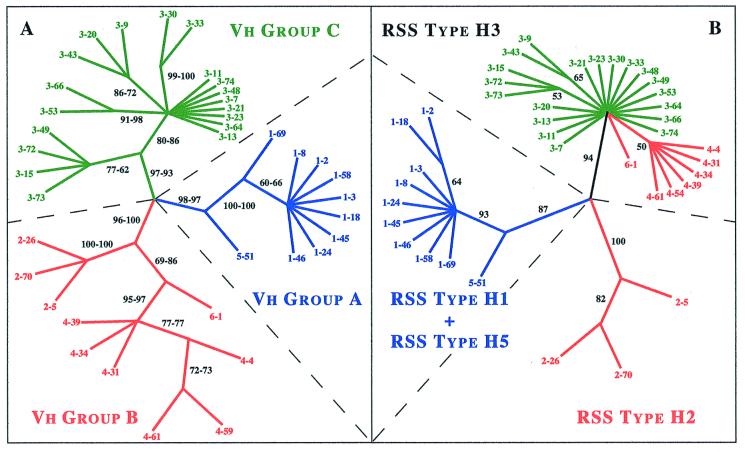
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic trees constructed from all known functional human Vh coding sequences (A) and RSSs (B). Phylogenetic analyses for the 39 functional genes of the human Vh locus were performed by using the maximum parsimony method with paup 3.1.1 (8). The trees presented here correspond to the bootstrap 50% majority-rule consensus trees, i.e., only groups with bootstrap proportions >50% are retained. (A) Tree constructed from the 261-bp sequences of Vh exon 2; see Materials and Methods. The sequences were examined by unweighted or weighted maximum parsimony analyses. The bootstrap proportions for the two different analyses are indicated on the branches, respectively at the left and right. The three major groups of Vh genes thus defined have been previously reported (3) and are here distinguished by the colors, blue for group A, red for group B, and green for group C. (B) Tree constructed from the 39-bp sequences of the Vh RSSs. It can be seen here that groups B and C, which are found with Vh coding sequences, are not retrieved for the associated RSSs.