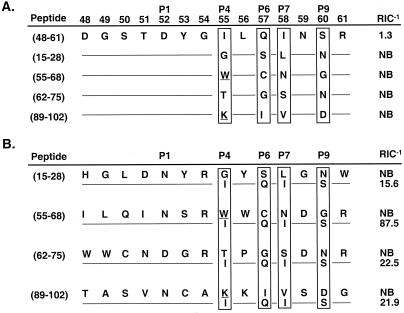
Figure 7.
Hindering auxiliary anchors participate in I-Ak epitope selection. (A) Auxiliary anchors of several nonbinding potential HEL epitopes are responsible for inhibiting I-Ak binding. Substitution of the auxiliary anchors from four predicted HEL epitopes into the high-affinity HEL(48-61) peptide completely prohibited binding to I-Ak. HEL(55-68), and HEL(89-102) contained a single inhibitory residue (underlined), Trp and Lys, respectively, that alone is likely to block binding (as shown in Fig. 3). However, HEL(15-28) and HEL(62-75) did not contain any of these individual inhibitory residues, therefore, their combinations of auxiliary anchors were hindering. (B) Replacing the inhibitory residues of potential HEL epitopes with favorable auxiliary anchors imparted the ability to bind I-Ak. The auxiliary anchors of four nonbinding peptides were replaced with favorable anchors derived from HEL(48-61). These chimeric peptides gained the ability to bind I-Ak. However, these peptides did not bind with the same affinity as the natural HEL(48-61) peptide did, likely because of additional effects of nonanchor residues.