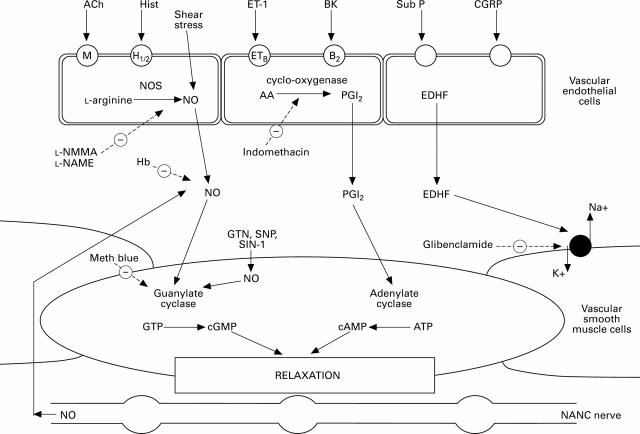
Figure 1 .
Mechanism of endothelium dependent relaxation showing the release of nitric oxide (NO), prostacyclin (PGI2 ) and endothelium derived hyperpolarising factor (EDHF) from the endothelium. Agonists act on specific endothelial cell receptors and may stimulate the release of one or all mediators to induce smooth muscle relaxation. Abbreviations: Acetylcholine (ACh), histamine (Hist), endothelin-1 (ET-1), bradykinin (BK), substance P (Sub P), calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP), nitric oxide synthase (NOS), arachidonic acid (AA), L-NG monomethyl arginine (L-NMMA), L-NG nitroarginine methylester (L-NAME), haemoglobin (Hb), glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), sodium nitroprusside (SNP), 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1), methylene blue (Meth blue), cyclic guanosine/adenosine monophosphate (cGMP/cAMP), guanosine/adenosine triphosphate (GTP/ATP), non-adrenergic non-cholinergic (NANC), muscarinic receptor (M), histamine receptor (H1/2 ), endothelin B receptor (ETB ), bradykinin receptor (B2 ).