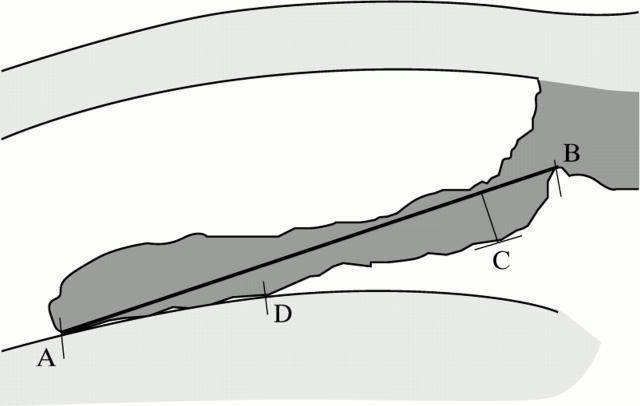
Figure 1 .
Iris deflection was measured by determining the maximum distance reached by the pigment epithelium (C) from a line joining the innermost point of the pigment epithelium in contact with the lens (A) with its outermost point at the iris root (B). Conventionally, the value was considered positive if the iris showed an anterior deflection (convexity) and negative in case of posterior deflection (concavity). Iridolenticular contact was quantified by measuring the distance between A and the outermost point of the pigment epithelium in contact with the lens (D).