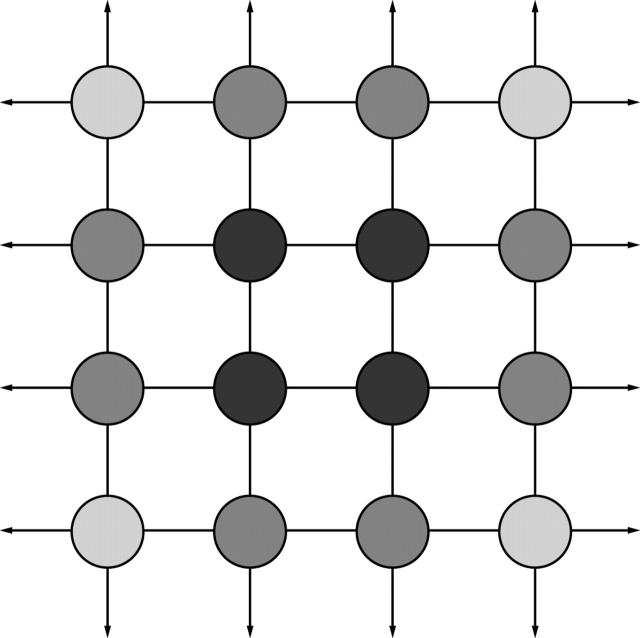
Figure 1 .
A simple two dimensional lattice illustrating surface reactivity. Molecules within the lattice are at a lower energy state (darker shade) than molecules at the surface which have more unoccupied bonding sites (arrows). Interfacial free energy is a measure of the number and reactivity of unoccupied bonding sites at the interface between a material surface and its surroundings. Polymers such as poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE, Teflon) have a have a relatively unreactive surface and are less prone to biological spoilation in aqueous systems than hydrophobic materials (for example, silicone, PMMA) with a higher interfacial free energy.