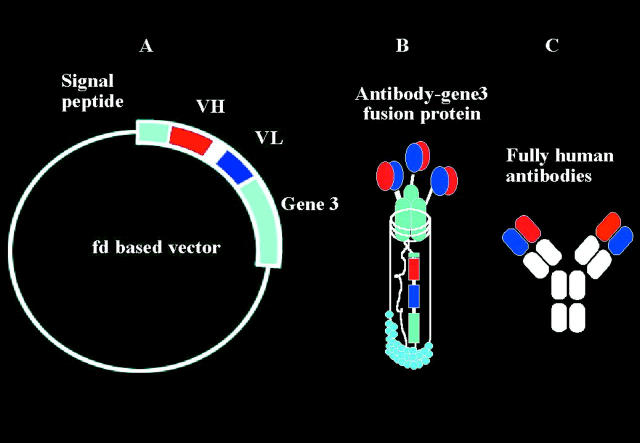
Figure 2 .
Phage antibodies. Fully human neutralising monoclonal antibodies can be made using the technique of phage display (Cambridge Antibody Technology, Melbourne UK). Human antibody light and heavy chains are identified from a large human antibody library. The human genes coding for these chains are then incorporated into a bacterial virus (phage) (A). When the phage infects a bacterium (usually, E coli), the bacterium makes the antibody protein which it displays on its surface (B). Specific clones binding to an antigen can then be amplified, and the whole antibody produced using recombinant methods (C).