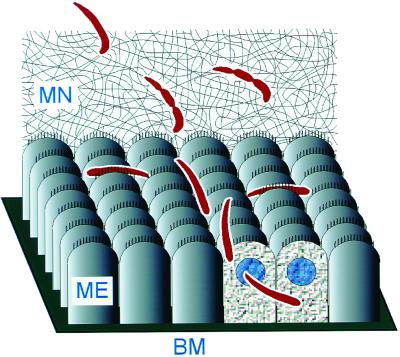
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of ookinete movement and midgut invasion. The ookinete first contacts the MN, through which it must navigate to reach the midgut surface. In the process of migrating through the MN, the ookinete develops constrictions along its length. Once on the surface of the midgut epithelium (ME), the parasite glides rapidly and tends to stay in the crevices between cells. Invasion occurs at the lateral apical membrane of a midgut cell. During its descent toward the basement membrane (BM), the ookinete often crosses to a neighboring cell. The refractive index of the invaded cells decreases, and their nuclei become more visible.