Abstract
AIMS—To assess the visual function in epileptic patients who have received vigabatrin; to compare this with the visual function in similar epileptic patients who have never received vigabatrin; to investigate whether the severity of visual field defect (VFD) is related to the dose of vigabatrin; to consider other factors that may correlate with the severity of VFD. METHODS—21 consecutive patients who had taken vigabatrin at some time in their lives were enrolled from the epilepsy clinic of the Royal Shrewsbury Hospital and were compared with a group of 11 otherwise similar patients with epilepsy who had never received vigabatrin. One patient taking vigabatrin was excluded from the study because her visual field results were unreliable because of multi-infarct dementia. 15 patients were taking vigabatrin at the time of the study (VC), the other five had taken vigabatrin some time in the past (VP). Each patient underwent static perimetry using either the two point or the three point full field 120 screening program on the Humphrey visual field analyser, followed by an ophthalmic examination to rule out ocular causes for VFDs. The visual fields from each patient were then analysed using a method devised to convert the VFD into percentage defect in both eyes. In patients with known cerebral pathology that may affect the visual pathway, only the unaffected homonymous hemifield was used. RESULTS—Nine of 20 (45%) patients in the vigabatrin group (VC and VP) complained of blurring of vision compared with two of 11 (18%) controls. Four patients (20%) in the vigabatrin group described flickering lights compared with one control (9%). None had a posterior vitreous detachment. Three of 30 (7.5%) eyes in the VC group had distant visual acuity of 6/12 or worse compared with three of 22 (9%) controls and five of 30 (16.7%) had near visual acuity worse than N6 compared with one of 22 (4.5%) in the control group. A mean of 1.73 Ishihara plates were misread in VC patients compared with 0.2 in the VP group and 0.18 in the controls. 11 of 15 (73.3%) patients in the VC group had greater than 10% VFDs as opposed to one of 11 (9.1%) controls (χ2 test, p=0.002). In 12 of 15 (80%) VC patients the percentage VFD was greater in the nasal hemifields than the temporal hemifields compared with six of 11 (54.5%) controls. Significant correlation was found between the severity of VFD and the total dose of vigabatrin ingested for the 20 patients exposed to vigabatrin (VC and VP: Spearman correlation coefficient=0.525; p=0.002), for the 15 patients taking vigabatrin at the time of examination (VC: Spearman correlation coefficient=0.568; p=0.002). CONCLUSION—This pilot study suggested that epileptic patients taking vigabatrin are at much higher risk of developing VFDs compared with epileptic patients on other antiepileptic drugs. The total ingested dose of vigabatrin correlated significantly with the severity of VFDs especially in those patients who had not stopped taking vigabatrin. In our group we found that those who had taken a total dose of 1500 g or more of vigabatrin were at risk of developing significant visual field defects.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (131.4 KB).
Figure 1 .
The percentage CTVFD results for all patients.
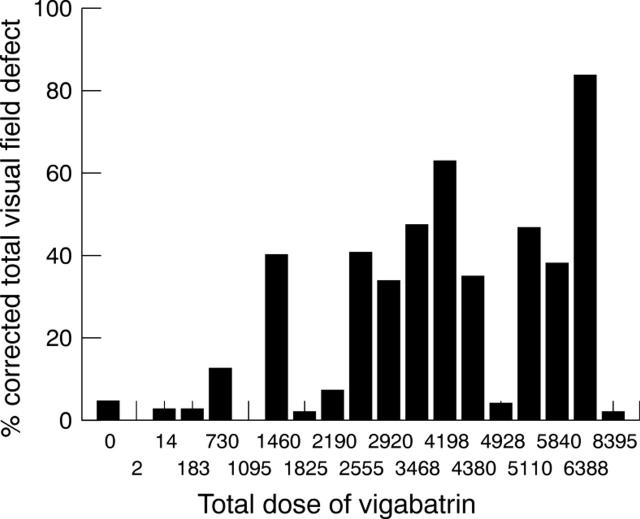
Figure 2 .
The total dose of vigabatrin (g) versus percentage CTVFD.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chadwick D. Safety and efficacy of vigabatrin and carbamazepine in newly diagnosed epilepsy: a multicentre randomised double-blind study. Vigabatrin European Monotherapy Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Jul 3;354(9172):13–19. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)10531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneshvar H., Racette L., Coupland S. G., Kertes P. J., Guberman A., Zackon D. Symptomatic and asymptomatic visual loss in patients taking vigabatrin. Ophthalmology. 1999 Sep;106(9):1792–1798. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(99)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eke T., Talbot J. F., Lawden M. C. Severe persistent visual field constriction associated with vigabatrin. BMJ. 1997 Jan 18;314(7075):180–181. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7075.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M. L., Gaily E., Liukkonen E. Treatment of infantile spasms: results of a population-based study with vigabatrin as the first drug for spasms. Epilepsia. 1999 Jul;40(7):950–957. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1999.tb00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo B. Vigabatrin in the treatment of infantile spasms. Pediatr Neurol. 1999 Feb;20(2):106–110. doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(98)00116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss G. L., Johnson M. A., Miller N. R. Vigabatrin-associated retinal cone system dysfunction: electroretinogram and ophthalmologic findings. Neurology. 1998 Mar;50(3):614–618. doi: 10.1212/wnl.50.3.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remler B. F., Leigh R. J., Osorio I., Tomsak R. L. The characteristics and mechanisms of visual disturbance associated with anticonvulsant therapy. Neurology. 1990 May;40(5):791–796. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.5.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruether K., Pung T., Kellner U., Schmitz B., Hartmann C., Seeliger M. Electrophysiologic evaluation of a patient with peripheral visual field contraction associated with vigabatrin. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998 Jun;116(6):817–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. A., Brodie M. J. New antiepileptic drugs. Baillieres Clin Neurol. 1996 Dec;5(4):723–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylinen A., Salmenperä T., Mumford J. P., Riekkinen P. J. Long-term treatment with vigabatrin - 10 years of clinical experience. Seizure. 1999 May;8(3):181–183. doi: 10.1053/seiz.1998.0260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamponi N., Cardinali C. Open comparative long-term study of vigabatrin vs carbamazepine in newly diagnosed partial seizures in children. Arch Neurol. 1999 May;56(5):605–607. doi: 10.1001/archneur.56.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]