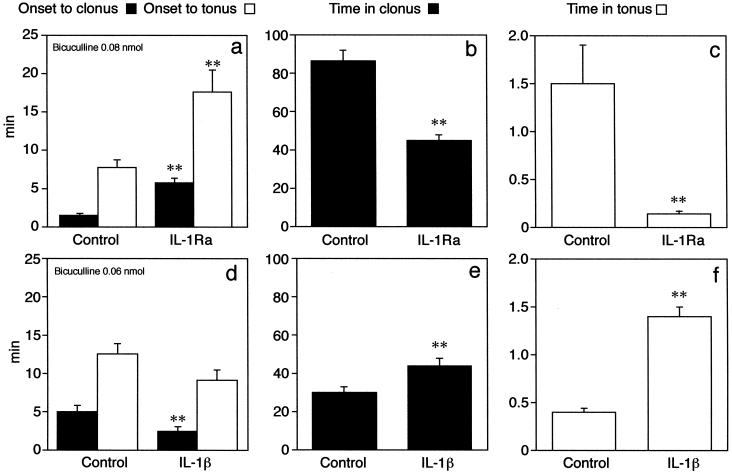
Figure 2.
Effects of unilateral intrahippocampal injection of 0.3 nmol IL-1Ra (a–c) or 3 pmol IL-1β (d–f) on motor seizure response of B6/CBA F1 mice to bicuculline methiodide. Data are the mean ± S.E.M. This strain of mice was the same used for engineering transgenic mice overexpressing the human secretable form of IL-1Ra. The anticonvulsant effect of IL-1Ra is denoted by the significant delay in the onset of motor seizures (a) and the reduction in their duration (b and c). All 13 mice in the control group showed both clonic and tonic seizures, whereas 2 mice of 14 did not show tonic seizures after IL-1Ra. The proconvulsant effect of IL-1β is depicted by earlier onset of clonic seizures (d) and by the increase in the duration of motor seizures (e and f). All nine mice in each experimental group showed both clonic and tonic seizures. The proconvulsant effect of IL-1β was assessed by using a submaximal convulsant dose of bicuculline (0.06 nmol) compared with the dose of 0.08 nmol used for testing the anticonvulsant activity of IL-1Ra. Control mice are injected with the corresponding heat-inactivated cytokine before bicuculline methiodide, and they do not differ from B6/CBA F1 mice (n = 6) receiving vehicle (sterile saline) before bicuculline methiodide. Time in clonus or in tonus was reckoned by adding the duration of each convulsive episode occurring during the 120-min observation period. **, P < 0.01 by Student's t test vs. respective controls.