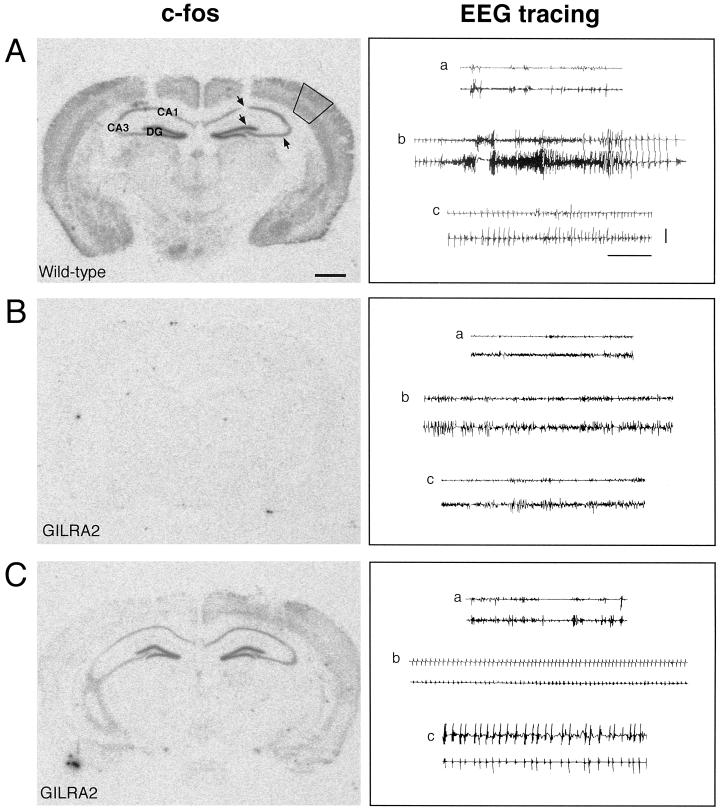
Figure 3.
C-fos mRNA expression after intrahippocampal injection of bicuculline methiodide in B6/CBA wild-type and transgenic mice overexpressing IL-1Ra in astrocytes (GILRA2). First column: C-fos was widely and massively expressed in the central nervous system after injection of bicuculline methiodide in wild-type B6/CBA mice (n = 5) (A). In contrast, mice overexpressing IL-1Ra (GILRA2, n = 7) showed no induction (B, n = 4) or considerably milder induction (C, n = 3) in most forebrain areas, particularly in the neocortex and hippocampus. No specific hybridization signal was found in naive mice (not shown). In A, solid lines in the neocortex and arrows in the hippocampus represent the areas where the hybridization signal was quantified (see text). Second column: Representative EEG tracings of the hippocampus in each row depict epileptic activity after injection of bicuculline methiodide in the corresponding wild-type (A) and GILRA2 mice (B and C) (see Table 1 for quantification of motor seizures). (a) Baseline recording before bicuculline injection; (b) ictal activity recorded in wild-type mice (A) was absent in one GILRA2 (B), whereas it was significantly reduced in number and duration in the remaining animals; (c) interictal spiking was interposed between seizures in wild-type mice (A), and it was present throughout the EEG recording in GILRA2 mice (C). Lower and upper traces in each cluster are the injected and contralateral hippocampus, respectively. (Horizontal bar = 10 sec; vertical bar = 100 μV.)