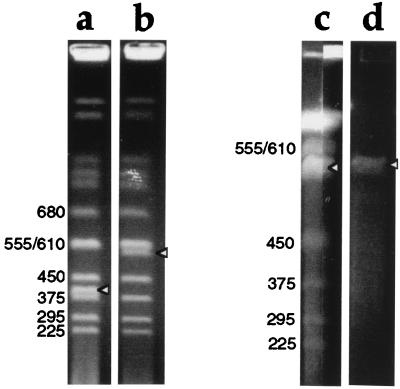
Figure 2.
Ethidium bromide staining of pulsed-field gels showing YAC DNA amplification and purification. Sizes in kilobases of yeast chromosomes are indicated, and bands corresponding to YAC DNA are indicated with arrowheads. (a and b) YAC clones before amplification, run on a 0.9% agarose gel in 0.5× TBE, at 6V/cm, 4°C for 24 h with 60 s switch time. (a) DNA from yeast containing a 400-kb YAC; (b) DNA from the 550-kb YAC HSC7E526. The intensity of ethidium bromide staining of the 550 kb YAC (b) is approximately half that of the band above, which contains two yeast chromosomes (555 and 610 kb) unresolved from one another. (c) DNA from pYIV3- and pYAM4-modified HSC7E526, run on a preparative scale in a 1% agarose gel in 0.25× TAE, at 6V/cm, 4°C for 32 h with 30 and 55 s switch time. Thirty-nine agarose plugs (0.5 cm × 0.15 cm × 1 cm) containing YAC DNA were loaded into a sample well 19.5 cm wide and sealed with agarose. After electrophoresis, the central 17 cm of the gel was kept for the purification of YAC DNA, and the remainder of the gel was stained with ethidium bromide and photographed. The two stained portions of the gel, each containing about 0.5 cm of the preparative lane, are shown. The intensity of staining of the YAC DNA is 1.5 to ≈2× that of the band above. (d) Gel-purified YAC DNA before microinjection into fertilized eggs.