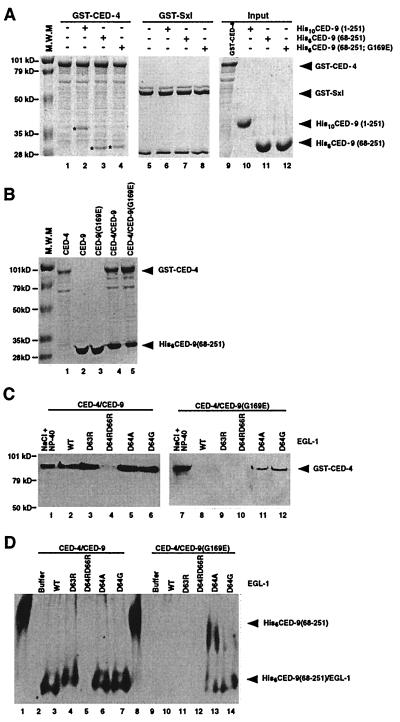
Figure 2.
Interactions of CED-9 with CED-4 and EGL-1-induced release of CED-4 from CED-4/CED-9 complexes. (A) His6CED-9(68–251; G169E) binds GST-CED-4 as well as His6CED-9(68–251). Purified CED-9 proteins (2.5 μg) were incubated with an equivalent amount of GST-CED-4 or GST-Sxl immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads. Protein complexes were washed three times with CED-3 buffer (23) containing 0.01% Triton X-100 and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining. The CED-9 proteins pulled down by GST-CED-4 are indicated with asterisks (lanes 2–4). (B) CED-4 copurifies with CED-9 proteins in 1:1 ratios. GST-CED-4 and His6CED-9(68–251) or His6CED-9(68–251; G169E) were expressed alone or were coexpressed in E. coli and purified using affinity chromatography. (C) EGL-1 releases CED-4 from CED-4/CED-9 complexes. Five-hundred nanograms of wild-type or mutant EGL-1 was added to approximately 1 μg of purified GST-CED-4/His6CED-9(68–251) or GST-CED-4/His6CED-9(68–251; G169E) complexes immobilized on Ni-NTA beads, and the resulting supernatants were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis using anti-GST antibodies to assess the amount of GST-CED-4 released. As positive controls, 1 M NaCl and 1% Nonidet P-40 were used to disassociate GST-CED-4 from GST-CED-4/CED-9 complexes. (D) EGL-1 displaces CED-4 from CED-4/CED-9 complexes. Five-hundred nanograms of wild-type or mutant EGL-1 was added to approximately 1 μg of purified GST-CED-4/His6CED-9(68–251) or GST-CED-4/His6CED-9(68–251; G169E) complexes immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads, and the resulting supernatants were subjected to native PAGE and Western blot analysis using anti-His6 antibodies to visualize the amount of EGL-1/CED-9 complexes released. In lanes 1 and 8, purified CED-9 (250 ng) was loaded as a control for free CED-9 species. EGL-1/CED-9 complexes containing EGL-1(D63R), EGL-1(D64A), or EGL-1(D64G) migrate slower than complexes with wild-type EGL-1 as a result of loss of a negatively charged Asp residue.