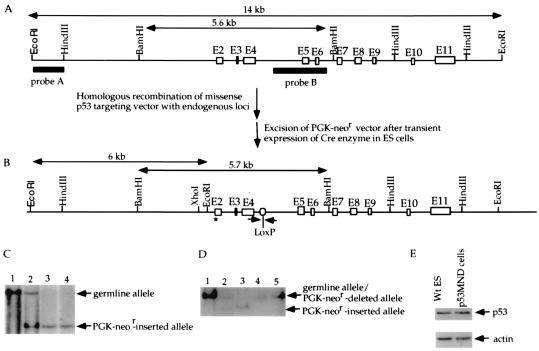
Figure 1.
Introduction of a missense mutation into the endogenous p53 gene of ES cells to change Ser-18 to Ala. (A) The mouse germ-line p53 locus. Blank boxes represent the p53 exons and two filled bars represent the probes for Southern blot analysis of the mutant/deleted allele. The germ-line 14-kb EcoRI fragment and 5.6-kb BamHI fragment are indicated. (B) Mutant p53 allele with the PGK-neor segment deleted. The size of the PGK-neor-deleted mutant BamHI fragment and the positions of PCR primers (arrows) flanking the remaining LoxP site are indicated. (C) Southern blotting analysis of the genomic DNA derived from wild-type (lane 1), heterozygous mutant (with the PGK-neor segment inserted; lane 2), and homozygous mutant (with the PGK-neor segment inserted; lanes 3 and 4) ES cells. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized with probe A. The positions of restriction fragments from the germ-line and mutant alleles are indicated with arrowheads. (D) Southern blotting analysis of genomic DNA derived from wild-type (lane 1), heterozygous mutant (with the PGK-neor segment inserted; lane 2), homozygous mutant (with the PGK-neor segment inserted; lane 3), and p53MND ES cells (lanes 4 and 5). Genomic DNA was digested with BamHI and hybridized with probe B. The positions of the BamHI fragments derived from the wild-type/PGK-neor-deleted mutant allele and the PGK-neor-inserted mutant allele are indicated. (E) Western blotting analysis of the constitutive p53 protein level in wild-type and p53MND ES cells. To ensure that equal amounts of protein were loaded, the blot was stripped and probed with anti-actin antibody. Lanes are labeled on the top; the primary antisera used (p53 or actin) is indicated at the right.