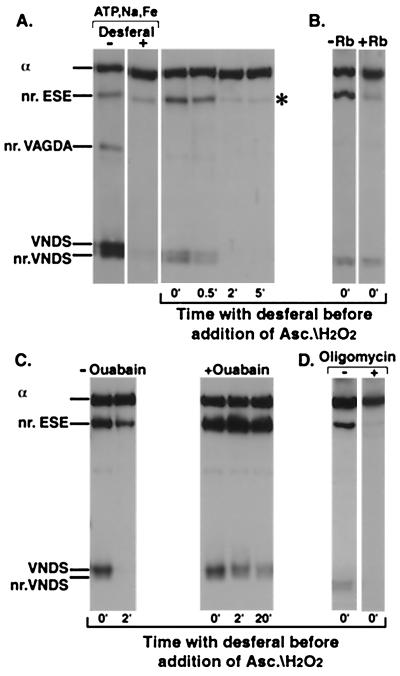
Figure 3.
Cleavage of Na,K-ATPase in the E2P conformation. (A) Lanes 1 and 2 only (Control). The enzyme was suspended at 0°C in a medium containing 130 mM NaCl, 1,000 μM ATP, 50 μM FeSO4, without or with 4 mM Desferal, and was incubated with 20 mM ascorbate/H2O2 for 5 min. (A–D) All other lanes. The enzyme was suspended at 0°C in a medium containing 130 mM NaCl, 1,000 μM ATP. FeSO4 (50 μM) was added to initiate formation of the phosphoenzyme. After 1 min incubation, 4 mM Desferal was added to terminate phosphoenzyme formation and trap free Fe2+. Ascorbate/H2O2 (20 mM) was added either together with the Desferal or later at indicated times. After 1 min further incubation to generate the cleavages, the gel sample buffer was added to stop the reaction. (A) Lanes 3–6, stability of tightly bound Fe2+. Ascorbate/H2O2 was added at indicated times after Desferal. (B) Dephosphorylation of E2P. Without or with 20 mM RbCl added with the Desferal/ascorbate/H2O2. (C) Inhibition of E2P hydrolysis. Ouabain (1 mM) was added after the incubation with Na+/ATP/Fe2+ to inhibit the phosphoenzyme, and, 1 min later, Desferal was added. Ascorbate/H2O2 was added together with the Desferal (0 min) or after the indicated times (2 min and 20 min). (D) Blocking of E1P-E2P; 200 μg/ml oligomycin was present in the incubation medium with Na+/ATP/Fe2+