Abstract
BACKGROUND AND AIMS—Evidence suggests that the intestinal actions of Clostridium difficile toxin A—stimulation of secretion and motility, and an acute inflammatory response—have a neurally mediated component. METHODS—Direct intracellular electrophysiological recording of electrical and synaptic behaviour in enteric neurones was performed in the submucous plexus of guinea pig small intestine during exposure to the toxin. RESULTS—Application of toxin A affected both the electrical behaviour of the neuronal cell bodies and inhibitory noradrenergic neurotransmission to the cell bodies. Altered electrical behaviour included depolarisation and increased excitability. Tetrodotoxin or a histamine H2 receptor antagonist did not affect the depolarisation evoked by toxin A. Failure of the histamine antagonist to suppress the actions of toxin A is evidence that its actions were not mediated by degranulation of intramural mast cells. The action of toxin A on neurotransmission was suppression of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials evoked in the neuronal cell bodies by stimulation of sympathetic nerve fibres that synapsed with the cell bodies. The inhibitory postsynaptic potentials were mediated by norepinephrine (noradrenaline) acting at postsynaptic alpha adrenoceptors on the cell bodies. Hyperpolarising responses evoked in the cell bodies by micropressure application of norepinephrine were unaffected by toxin A. This fulfils criteria for a presynaptic inhibitory action of toxin A to suppress release of norepinephrine from sympathetic postganglionic axons. CONCLUSIONS—Results suggest that the neural component of the action of toxin A involves both direct excitation of enteric neurones and suppression of norepinephrine release from postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibres in the enteric nervous system. Keywords: enteric nervous system; enterotoxins; diarrhoea; intestine
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (188.6 KB).
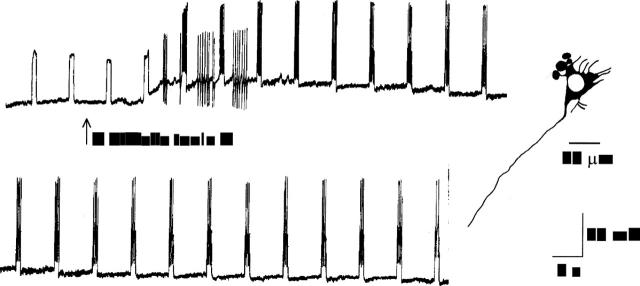
Figure 1 .
Application of C difficile toxin A by pressure microejection depolarised and enhanced the excitability of neurones in the submucous plexus. The top and bottom records are continuous. The neurone failed to discharge action potentials in response to intraneuronal injection of rectangular depolarising current pulses before application of the toxin. After application, slowly activating depolarisation of the membrane potential occurred. The depolarisation was accompanied by enhanced excitability as reflected by repetitive action potential discharge evoked by intraneuronal current injection and spontaneous spike discharge. The neurone had uniaxonal morphology.
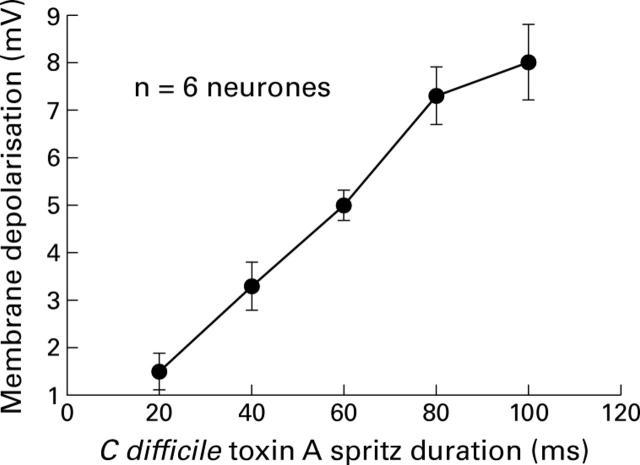
Figure 2 .
The amplitude of the depolarising response to C difficile toxin A increased with increasing amounts of toxin when the toxin was applied by pressure microejection. The amount of toxin applied was increased by progressively increasing the duration of the microejection pulses.
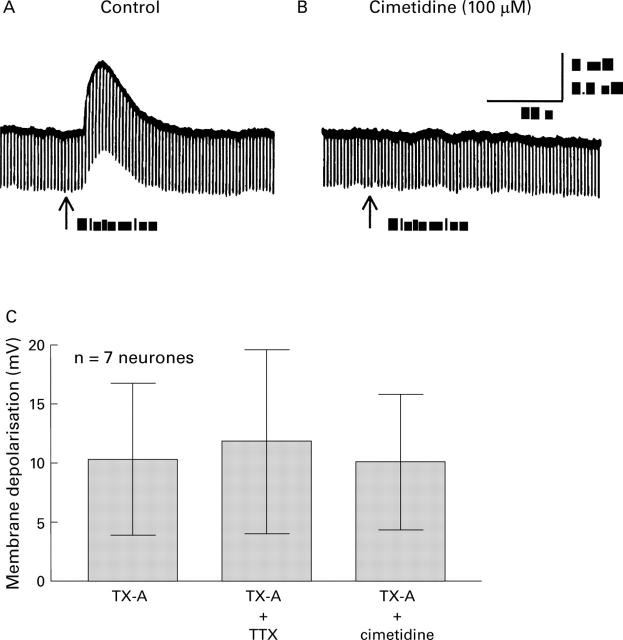
Figure 3 .
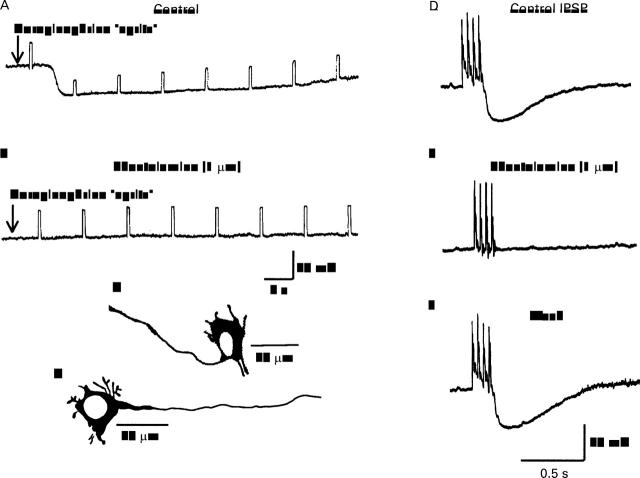
The depolarising responses evoked by histamine and toxin A (TX-A). (A) Microejection pulse of 100 µM histamine depolarised the neurone. Depolarisation was associated with increased input resistance as reflected by increased amplitude of electrotonic potentials produced by intraneuronal injection of constant current hyperpolarising pulses. (B) Pretreatment with 100 µM cimetidine blocked the response to histamine. (C) Neither 100 µM cimetidine nor 2 µM tetrodotoxin (TTX) significantly suppressed the depolarising action of C difficile TX-A. This suggested that the action of TX-A was directly on the neurones from which the recordings were obtained rather than because of release of histamine from mast cells or transmitter release from presynaptic terminals.
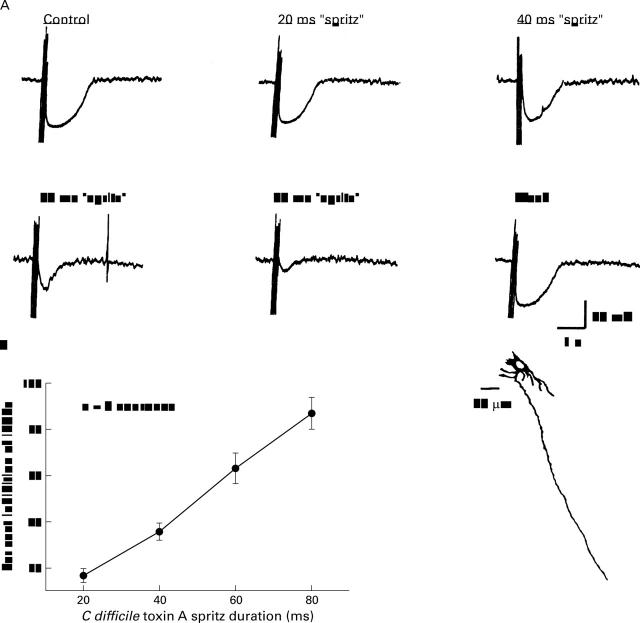
Figure 4 .
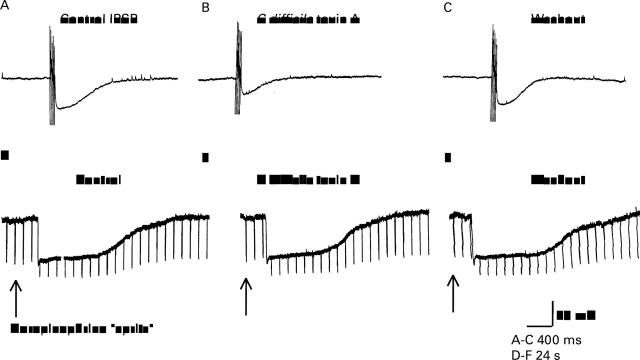
Focal electrical stimulation of sympathetic noradrenergic synaptic inputs to submucous plexus neurones evoked inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP). (A) Application of C difficile toxin A (TX-A) suppressed the stimulus evoked IPSPs. Suppression of the IPSP was concentration dependent as reflected by a progressive decrease in the amplitude of hyperpolarisation with progressively increased duration of micropressure pulses ("spritz") from 20 to 80 ms in a single neurone. (B) Quantitative concentration-response data for eight neurones. The neurone in A had uniaxonal morphology.
Figure 5 .
The alpha adrenergic blocking drug, phentolamine, blocked both the hyperpolarising responses to micropressure application of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and stimulus evoked inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP). (A) Micropressure ("spritz") application of 10 µM norepinephrine evoked a hyperpolarising response accompanied by decreased input resistance. Decreased input resistance was reflected by decreased amplitude of electrotonic potentials produced by intrasomal injection of constant current depolarising pulses. (B) Blockade of norepinephrine evoked response by phentolamine. (C) The neurone in A and B had uniaxonal morphology. (D) Focal electrical stimulation of an interganglionic connective evoked and IPSP. (E) Blockade of the IPSP by phentolamine. (F) Reversal of phentolamine induced blockade following washout of the drug. (G) The neurone in D and F had uniaxonal morphology.
Figure 6 .
Toxin A (TX-A) suppressed stimulus evoked noradrenergic inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) but not the hyperpolarising responses to exogenously applied norepinephrine (noradrenaline). (A) Control IPSP. (B) Suppression of IPSP by micropressure pulse of TX-A. (C) Recovery of IPSP after washout of TX-A. (D) Hyperpolarising response to micropressure pulse of norepinephrine. (E) Hyperpolarising response to norepinephrine during exposure to TX-A was unchanged. (F) Hyperpolarising response to norepinephrine after washout of TX-A. All records are from the same neurone. Downward deflections in D-F are electrotonic potentials produced by intraneuronal injection of constant current hyperpolarising pulses.
Figure 7 .
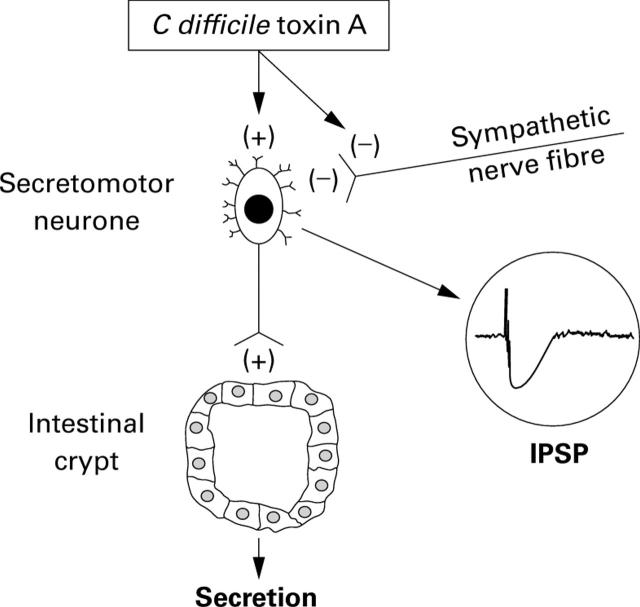
Heuristic model for action of C difficile toxin A (TX-A) in the enteric nervous system. TX-A acts directly to increase excitability of neurones and to suppress release of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) at sympathetic synapses on submucous neurones. Stimulation of submucosal secretomotor neurones is expected to evoke secretion from mucosal crypts and may account in part for diarrhoeal symptoms associated with C difficile enteritis. Inactivation of sympathetic braking action on secretomotor neurones facilitates secretion and may also contribute to diarrhoeal symptoms.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castagliuolo I., Keates A. C., Qiu B., Kelly C. P., Nikulasson S., Leeman S. E., Pothoulakis C. Increased substance P responses in dorsal root ganglia and intestinal macrophages during Clostridium difficile toxin A enteritis in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 29;94(9):4788–4793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Letourneau R., Kelly C., O'Keane J. C., Jaffer A., Theoharides T. C., Pothoulakis C. Neuronal involvement in the intestinal effects of Clostridium difficile toxin A and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1994 Sep;107(3):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieling T., Cooke H. J., Wood J. D. Neuroimmune communication in the submucous plexus of guinea pig colon after sensitization to milk antigen. Am J Physiol. 1994 Dec;267(6 Pt 1):G1087–G1093. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.6.G1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieling T., Palmer J. M., Cooke H. J., Wood J. D. Neuroimmune communication in the submucous plexus of guinea pig colon after infection with Trichinella spiralis. Gastroenterology. 1994 Dec;107(6):1602–1609. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90798-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. Presynaptic inhibition at mammalian peripheral synapse? Nature. 1974 Aug 2;250(465):430–431. doi: 10.1038/250430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A., Williams J. T. The action of substance P on neurons of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Nov 30;206(1163):191–208. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. P., Becker S., Linevsky J. K., Joshi M. A., O'Keane J. C., Dickey B. F., LaMont J. T., Pothoulakis C. Neutrophil recruitment in Clostridium difficile toxin A enteritis in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1257–1265. doi: 10.1172/JCI117080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. P., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T. Clostridium difficile colitis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 27;330(4):257–262. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401273300406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manber L., Gershon M. D. A reciprocal adrenergic-cholinergic axoaxonic synapse in the mammalian gut. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E738–E745. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Jaffer A., O'Keane J. C., Snider R. M., Leeman S. E. CP-96,345, a substance P antagonist, inhibits rat intestinal responses to Clostridium difficile toxin A but not cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):947–951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., Karmeli F., Kelly C. P., Eliakim R., Joshi M. A., O'Keane C. J., Castagliuolo I., LaMont J. T., Rachmilewitz D. Ketotifen inhibits Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced enteritis in rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1993 Sep;105(3):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90886-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Eglow R., Gao N., Rubins J. B., Theoharides T. C., Dickey B. F. Characterization of rabbit ileal receptors for Clostridium difficile toxin A. Evidence for a receptor-coupled G protein. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):119–125. doi: 10.1172/JCI115267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothoulakis Charalabos, Castagliuolo Ignazio, LaMont J. Thomas. Nerves and Intestinal Mast Cells Modulate Responses to Enterotoxins. News Physiol Sci. 1998 Apr;13(NaN):58–63. doi: 10.1152/physiologyonline.1998.13.2.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., North R. A. Mechanism of synaptic inhibition by noradrenaline acting at alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):85–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wershil B. K., Castagliuolo I., Pothoulakis C. Direct evidence of mast cell involvement in Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced enteritis in mice. Gastroenterology. 1998 May;114(5):956–964. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Histamine signals in enteric neuroimmune interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;664:275–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb39767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafirov D. H., Cooke H. J., Wood J. D. Elevation of cAMP facilitates noradrenergic transmission in submucous neurons of guinea pig ileum. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):G442–G446. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.3.G442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]