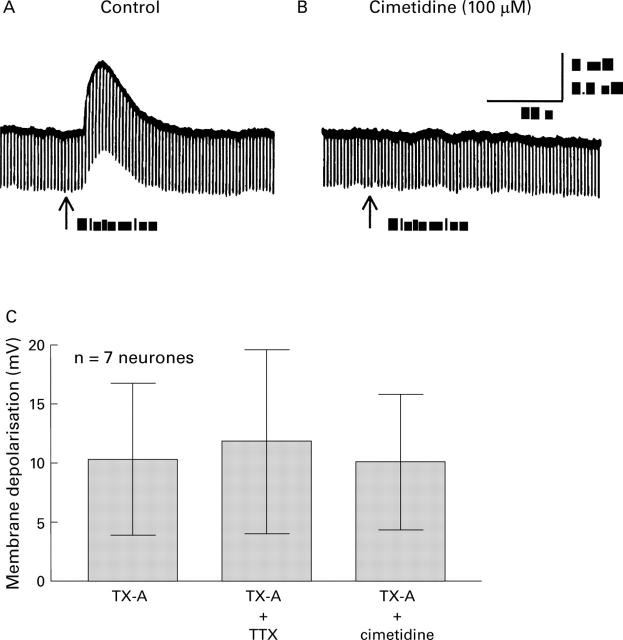
Figure 3 .
The depolarising responses evoked by histamine and toxin A (TX-A). (A) Microejection pulse of 100 µM histamine depolarised the neurone. Depolarisation was associated with increased input resistance as reflected by increased amplitude of electrotonic potentials produced by intraneuronal injection of constant current hyperpolarising pulses. (B) Pretreatment with 100 µM cimetidine blocked the response to histamine. (C) Neither 100 µM cimetidine nor 2 µM tetrodotoxin (TTX) significantly suppressed the depolarising action of C difficile TX-A. This suggested that the action of TX-A was directly on the neurones from which the recordings were obtained rather than because of release of histamine from mast cells or transmitter release from presynaptic terminals.