Abstract
BACKGROUND—Noxious intestinal distention elicits a reflex depressor response in the sodium pentobarbitone anaesthetised rat, which can be used as an index of visceral nociception. 5-HT3 receptor antagonists inhibit this reflex. Repeated colorectal distention (CRD) induces Fos like immunoreactivity (Fos-LI) in the rat spinal cord. AIMS—To examine the effect of the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist alosetron on the depressor response to CRD, and on Fos expression in the lumbosacral spinal cord. METHODS—Male rats were anaesthetised with sodium pentobarbitone, and mean arterial blood pressure monitored during repeated colorectal balloon inflation before and after treatment with alosetron or saline. Rats anaesthetised with urethane and treated with alosetron or saline underwent a repeated CRD paradigm, after which the lumbosacral spinal cord was removed and processed for visualisation of Fos-LI. RESULTS—CRD elicited reproducible, volume dependent falls in arterial blood pressure, and repeated distention-effect curves were constructed. Alosetron (1-100 µg/kg intravenously) inhibited the depressor response to CRD in a dose related manner, with an ID50 value of 3.0 µg/kg. Following repeated CRD, numbers of Fos-LI neurones were significantly increased to 1246 (total in 12 sections at 120 µm intervals from L6 to S1) compared with 49 in sham distended animals. Pretreatment with alosetron (100 µg/kg) significantly reduced numbers of Fos-LI neurones to 479.8. CONCLUSION—The 5-HT3 receptor antagonist alosetron inhibits the depressor response to CRD in a potent and dose dependent manner. It also inhibits CRD induced Fos-LI in the spinal cord. These results suggest that 5-HT3 receptors are involved in visceral nociceptive transmission, perhaps located on primary afferent or spinal neurones. Keywords: colorectal distention; alosetron; Fos; 5-HT3; spinal cord; pseudoaffective reflex
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (183.1 KB).
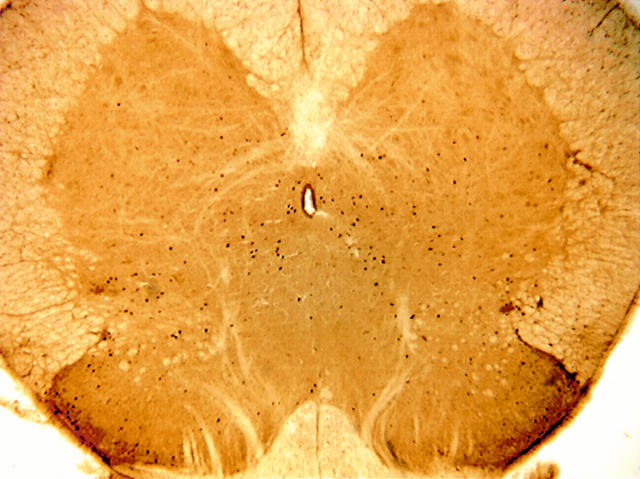
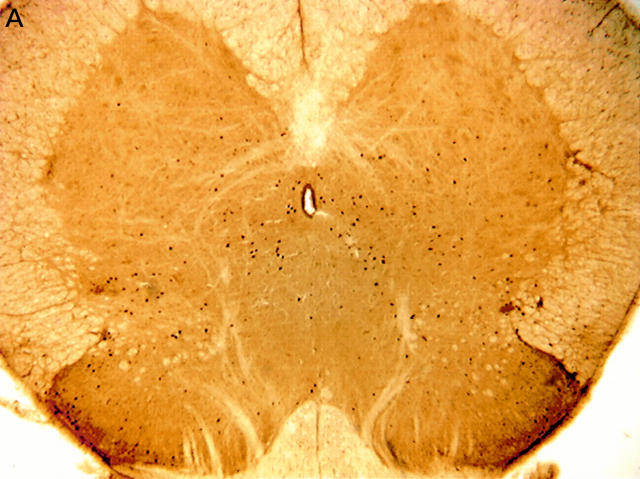
Figure 1 .
(A) Bilateral Fos-like immunoreactivity (Fos-LI) in a section of L6-S1 spinal cord following repeated (2 h, 80 mm Hg for 30 s every 120 s) colorectal distention. (B) Areas used to count regional Fos-LI: area 1, superficial laminae I and II; area 2, laminae III and IV; area 3, lateral laminae V-VII (intermediolateral horn) and lateral ventral horn; area 4, medial laminae V-VII and X, and medial ventral horn.
Figure 2 .
Colorectal distention (30 s every 5 min) evokes volume related decreases in mean arterial pressure which are highly reproducible (n=4).
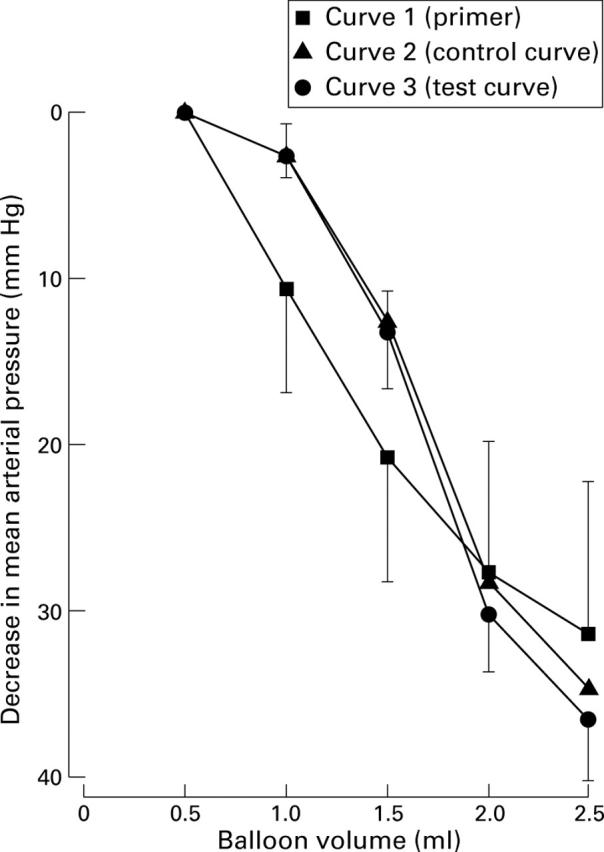
Figure 3 .
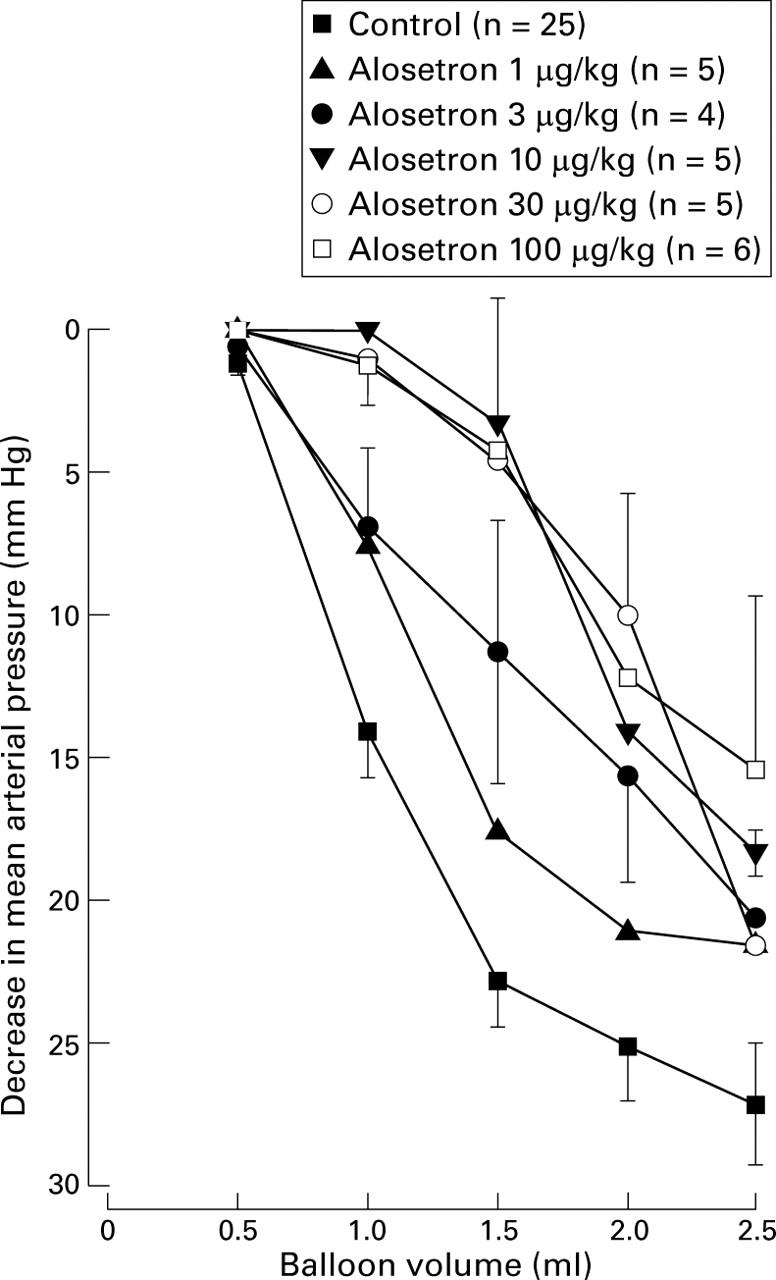
Influence of alosetron (1-100 µg/kg) on the hypotensive response to colorectal distention.
Figure 4 .
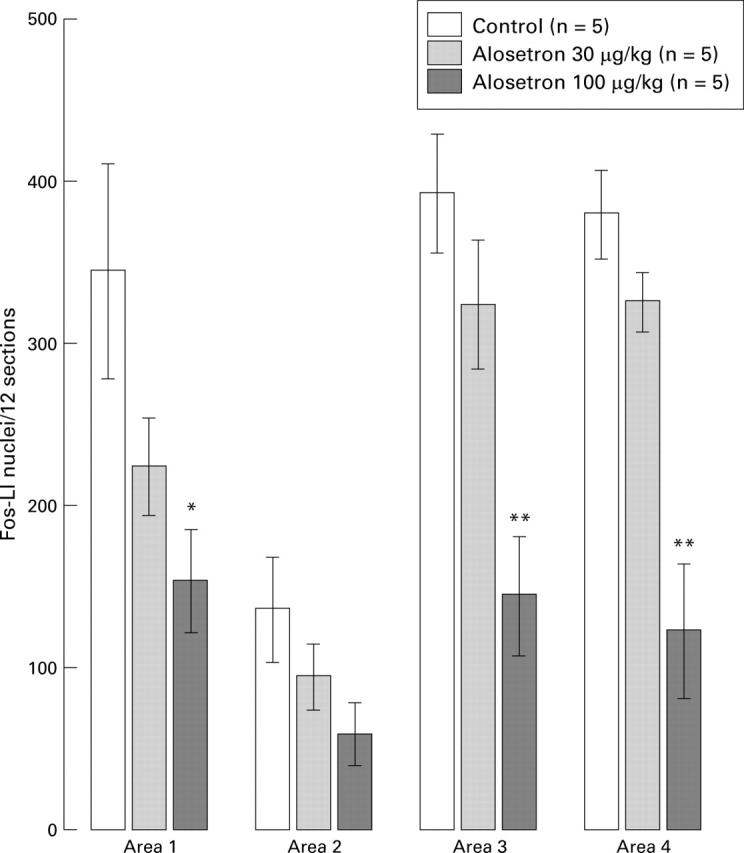
Alosetron reduces the number of Fos-like immunoreactive (Fos-LI) nuclei (in 12 sections across L6-S1) evoked following 2 h (80 mm Hg, for 30 s every 120 s) repeated colorectal distention. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, significant reduction of Fos-LI.
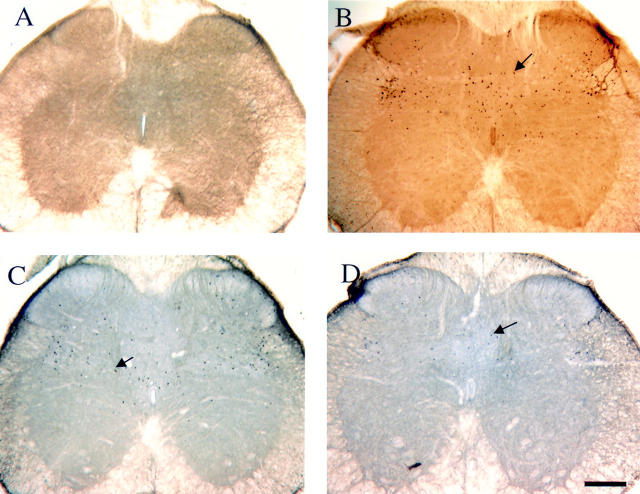
Figure 5 .
Representative bitmap images illustrating distribution of Fos-like (Fos-LI) immunoreactivity in all treatment groups: (A) sham distended; (B) control colorectal distention (CRD); (C) CRD/alosetron, 30 µg/kg; (D) CRD/alosetron 100 µg/kg. Horizontal scale bar, 150 µm; arrows indicate examples of Fos-LI nuclei.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banner S. E., Carter M., Sanger G. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine3 receptor antagonism modulates a noxious visceral pseudoaffective reflex. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Mar;34(3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00159-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birder L. A., Roppolo J. R., Iadarola M. J., de Groat W. C. Electrical stimulation of visceral afferent pathways in the pelvic nerve increases c-fos in the rat lumbosacral spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Aug 19;129(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birder L. A., de Groat W. C. Induction of c-fos expression in spinal neurons by nociceptive and nonnociceptive stimulation of LUT. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 2):R326–R333. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.265.2.R326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissonade F. M., Sharkey K. A., Davison J. S. Fos expression in ferret dorsal vagal complex after peripheral emetic stimuli. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):R1118–R1126. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.4.R1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton N. M., Sargent R., Butler A., Gale J., Maxwell M. P., Hunt A. A., Barrett V. J., Cambridge D., Bountra C., Humphrey P. P. The pharmacological properties of the novel selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, alosetron, and its effects on normal and perturbed small intestinal transit in the fasted rat. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 1999 Jun;11(3):207–217. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2982.1999.00148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement C. I., Keay K. A., Owler B. K., Bandler R. Common patterns of increased and decreased fos expression in midbrain and pons evoked by noxious deep somatic and noxious visceral manipulations in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1996 Mar 11;366(3):495–515. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960311)366:3<495::AID-CNE9>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz F., Avelino A., Coimbra A. Desensitization follows excitation of bladder primary afferents by intravesical capsaicin, as shown by c-fos activation in the rat spinal cord. Pain. 1996 Mar;64(3):553–557. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(95)00157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvaux M., Louvel D., Mamet J. P., Campos-Oriola R., Frexinos J. Effect of alosetron on responses to colonic distension in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998 Sep;12(9):849–855. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1998.00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersberger A., Anton F., Tölle T. R., Zieglgänsberger W. Morphine, 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptor antagonists reduce c-fos expression in the trigeminal nuclear complex following noxious chemical stimulation of the rat nasal mucosa. Brain Res. 1995 Apr 10;676(2):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00118-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch G. K., Weiss M. L. Ureteral ligation induces Fos expression in the dorsal horn. Brain Res. 1996 Jun 3;723(1-2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamon M., Gallissot M. C., Menard F., Gozlan H., Bourgoin S., Vergé D. 5-HT3 receptor binding sites are on capsaicin-sensitive fibres in the rat spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 19;164(2):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90472-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. P., Pini A., Evan G. Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):632–634. doi: 10.1038/328632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin G. R., Rao Z. R., Shi J. W. Visceral noxious stimulation induced expression of Fos protein in medullary catecholaminergic neurons projecting to nucleus accumbens in the rat: a study with triple labeling method of HRP tracing combined with Fos and TH immunohistochemistry. Brain Res. 1994 Jun 20;648(2):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kia H. K., Miquel M. C., McKernan R. M., Laporte A. M., Lombard M. C., Bourgoin S., Hamon M., Vergé D. Localization of 5-HT3 receptors in the rat spinal cord: immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Neuroreport. 1995 Jan 26;6(2):257–261. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199501000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPKIN M., SLEISENGER M. H. Studies of visceral pain: measurements of stimulus intensity and duration associated with the onset of pain in esophagus, ileum and colon. J Clin Invest. 1958 Jan;37(1):28–34. doi: 10.1172/JCI103581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantéri-Minet M., Isnardon P., de Pommery J., Menétrey D. Spinal and hindbrain structures involved in visceroception and visceronociception as revealed by the expression of Fos, Jun and Krox-24 proteins. Neuroscience. 1993 Aug;55(3):737–753. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90439-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte A. M., Fattaccini C. M., Lombard M. C., Chauveau J., Hamon M. Effects of dorsal rhizotomy and selective lesion of serotonergic and noradrenergic systems on 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT3 receptors in the rat spinal cord. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1995;100(3):207–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01276459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laporte A. M., Koscielniak T., Ponchant M., Vergé D., Hamon M., Gozlan H. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of 5-HT3 receptors in the rat CNS using [125I]iodo-zacopride and [3H]zacopride as radioligands. Synapse. 1992 Apr;10(4):271–281. doi: 10.1002/syn.890100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Skofitsch G. Visceral pain reflex after pretreatment with capsaicin and morphine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;321(2):116–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00518478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lémann M., Dederding J. P., Flourié B., Franchisseur C., Rambaud J. C., Jian R. Abnormal perception of visceral pain in response to gastric distension in chronic idiopathic dyspepsia. The irritable stomach syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Sep;36(9):1249–1254. doi: 10.1007/BF01307517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez V., Wang L., Mayer E., Taché Y. Proximal colon distention increases Fos expression in the lumbosacral spinal cord and activates sacral parasympathetic NADPHd-positive neurons in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1998 Jan 19;390(3):311–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menétrey D., Gannon A., Levine J. D., Basbaum A. I. Expression of c-fos protein in interneurons and projection neurons of the rat spinal cord in response to noxious somatic, articular, and visceral stimulation. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 8;285(2):177–195. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz H., Naliboff B., Munakata J., Niazi N., Mayer E. A. Altered rectal perception is a biological marker of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jul;109(1):40–52. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90267-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Lawson D. C., Clary E. M., Mangel A. W., Pappas T. N. Central modulation of rectal distension-induced blood pressure changes by alosetron, a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. Dig Dis Sci. 1999 Jan;44(1):20–24. doi: 10.1023/a:1026633629141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss H. E., Sanger G. J. The effects of granisetron, ICS 205-930 and ondansetron on the visceral pain reflex induced by duodenal distension. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):497–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadelhaft I., Booth A. M. The location and morphology of preganglionic neurons and the distribution of visceral afferents from the rat pelvic nerve: a horseradish peroxidase study. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jun 20;226(2):238–245. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness T. J., Gebhart G. F. Colorectal distension as a noxious visceral stimulus: physiologic and pharmacologic characterization of pseudaffective reflexes in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 May 31;450(1-2):153–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness T. J., Gebhart G. F. Visceral pain: a review of experimental studies. Pain. 1990 May;41(2):167–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce P. A., Xie G. X., Levine J. D., Peroutka S. J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtype messenger RNAs in rat peripheral sensory and sympathetic ganglia: a polymerase chain reaction study. Neuroscience. 1996 Jan;70(2):553–559. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00329-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior A., Read N. W. Reduction of rectal sensitivity and post-prandial motility by granisetron, a 5 HT3-receptor antagonist, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Apr;7(2):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1993.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. Pain from distension of the pelvic colon by inflating a balloon in the irritable colon syndrome. Gut. 1973 Feb;14(2):125–132. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta J. N., Gebhart G. F. Characterization of mechanosensitive pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the colon of the rat. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Jun;71(6):2046–2060. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.6.2046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steadman C. J., Talley N. J., Phillips S. F., Zinsmeister A. R. Selective 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor antagonism with ondansetron as treatment for diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1992 Aug;67(8):732–738. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60797-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tecott L. H., Maricq A. V., Julius D. Nervous system distribution of the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1430–1434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. J., Pechman P., Iadarola M. J., Gebhart G. F. Fos-like proteins in the lumbosacral spinal cord following noxious and non-noxious colorectal distention in the rat. Pain. 1992 Jun;49(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. J., Stitt S., Gebhart G. F. Attenuation of c-Fos expression in the rat lumbosacral spinal cord by morphine or tramadol following noxious colorectal distention. Brain Res. 1995 Dec 1;701(1-2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00990-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]