Abstract
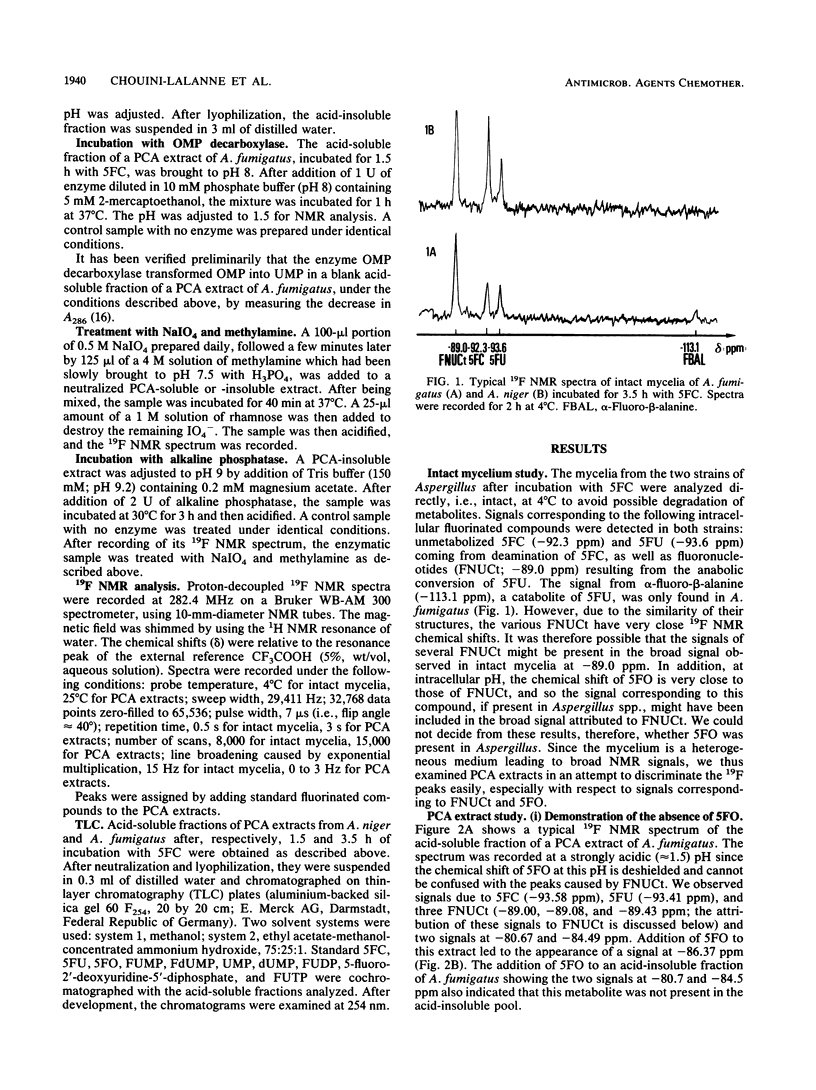
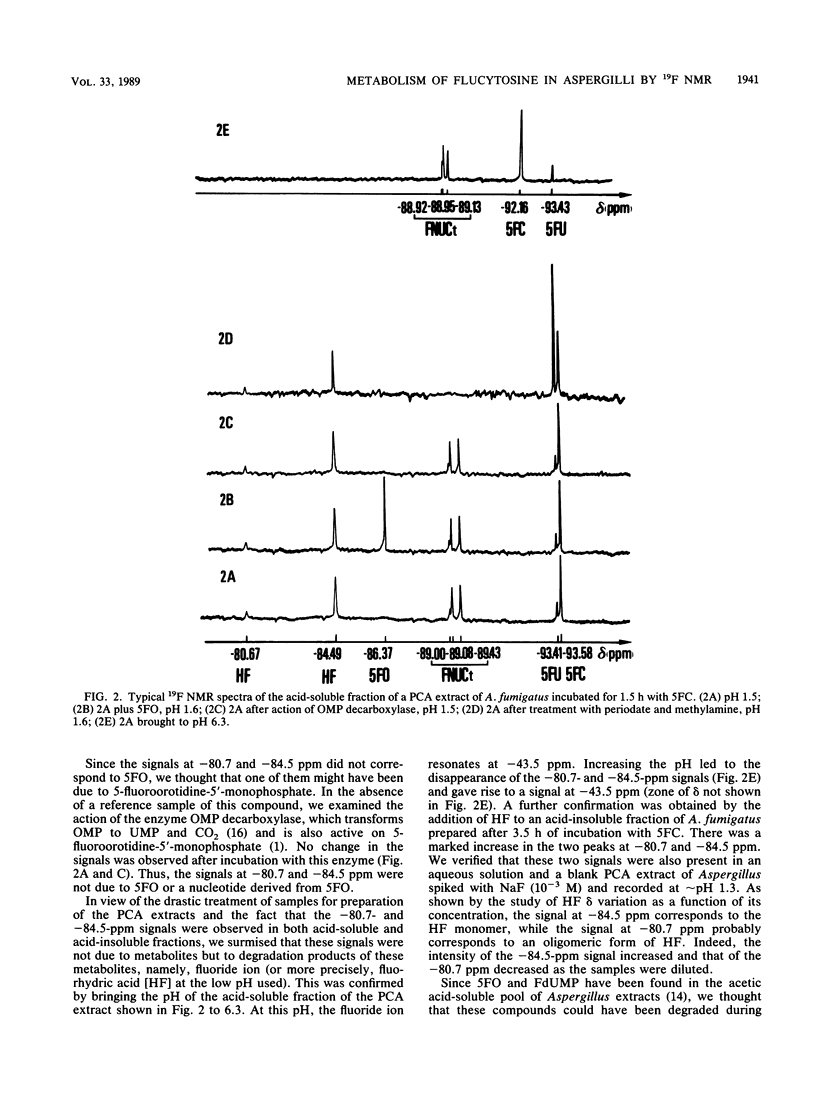
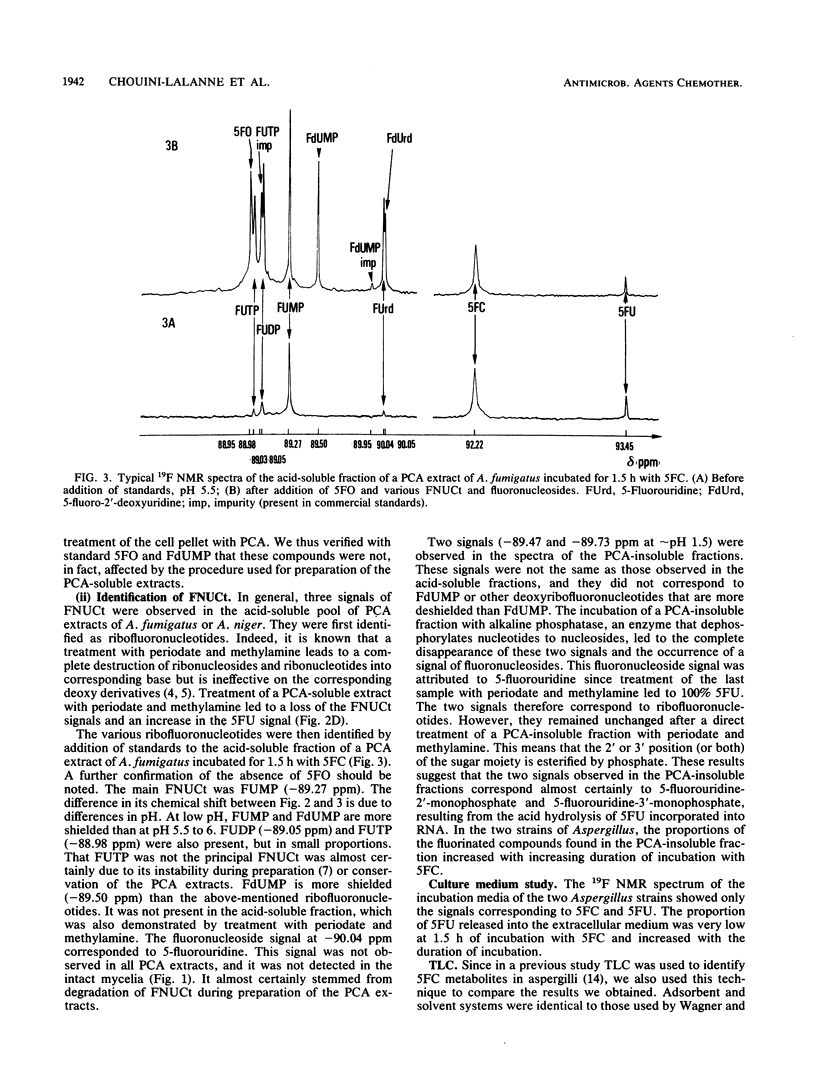
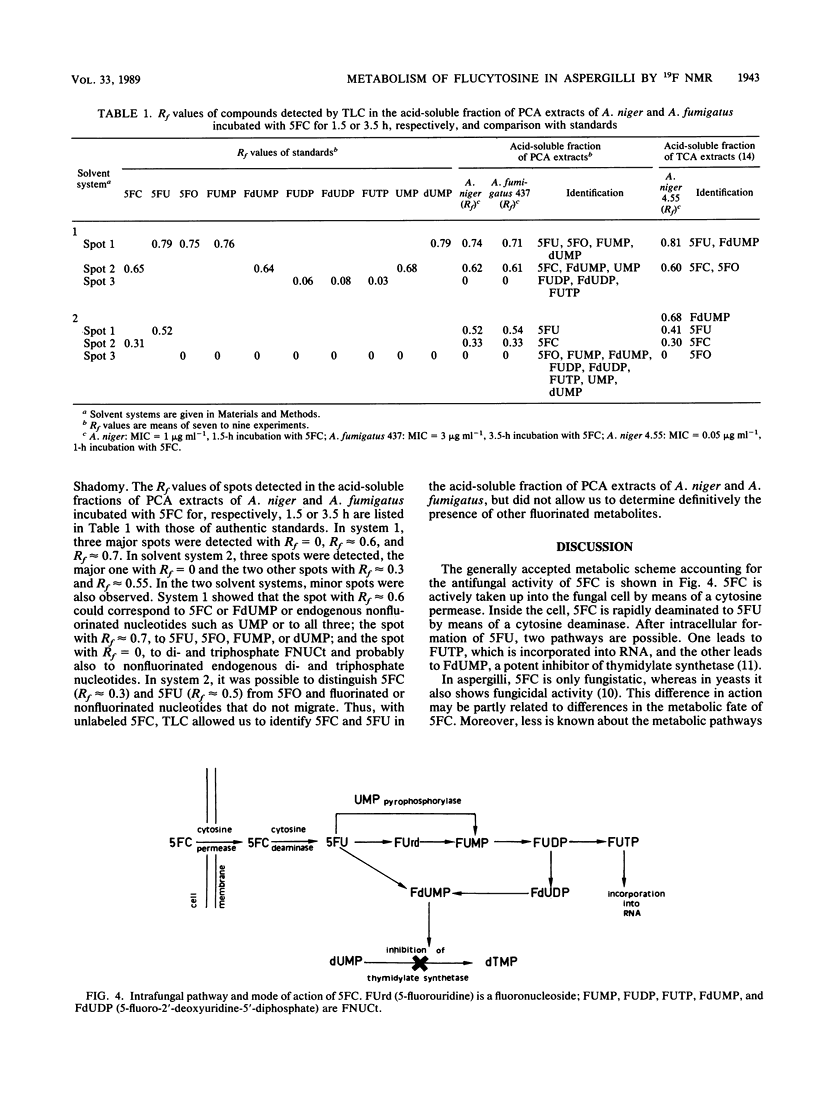
The metabolism of flucytosine (5FC) in two Aspergillus species (Aspergillus fumigatus and A. niger) was investigated by 19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In intact mycelia, 5FC was found to be deaminated to 5-fluorouracil and then transformed into fluoronucleotides; the catabolite alpha-fluoro-beta-alanine was also detected in A. fumigatus. Neither 5-fluoroorotic acid nor 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate was detected in perchloric acid extracts after any incubation with 5FC. 5FC, 5-fluorouracil, and the classical fluoronucleotides 5-fluorouridine-5'-mono-, di-, and triphosphates were identified in the acid-soluble pool. Two hydrolysis products of 5-fluorouracil incorporated into RNA, 5-fluorouridine-2'-monophosphate and 5-fluorouridine-3'-monophosphate, were found in the acid-insoluble pool. No significant differences in the metabolic transformation of 5FC were noted in the two species of Aspergillus. The main pathway of 5FC metabolism in the two species of Aspergillus studied is thus the biotransformation into ribofluoronucleotides and the subsequent incorporation of 5-fluorouridine-5'-triphosphate into RNA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAHL J. L., WAY J. L., PARKS R. E., Jr The enzymatic synthesis of 5-fluorouridine 5'-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2998–3002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Nollin S., Jacob W., Garrevoet T., Van Daele A., Dockx P. Influence of econazole and 5-fluorocytosine on the ultrastructure of Aspergillus fumigatus and the cytochemical localization of calcium ions as measured by laser microprobe mass analysis. Sabouraudia. 1983 Dec;21(4):287–302. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Vito M., Podo F., Torosantucci A., Carpinelli G., Whelan W. L., Kerridge D., Cassone A. A 19F nuclear magnetic resonance study of uptake and metabolism of 5-fluorocytosine in susceptible and resistant strains of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer R., Cadman E. Use of periodate and methylamine for the quantitation of intracellular 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1981 Dec 4;219(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)87937-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett C., Santi D. V. A rapid and sensitive high pressure liquid chromatography assay for deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):268–273. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisot D., Malet-Martino M. C., Crasnier P., Martino R. 19F nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of 5-fluorouracil metabolism in wild-type and 5-fluorouracil-resistant Nectria haematococca. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2474–2479. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2474-2479.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogolotti A. L., Jr, Nolan P. A., Santi D. V. Methods for the complete analysis of 5-fluorouracil metabolites in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):178–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90708-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak A., Scholer H. J., Wall M. Combination therapy of experimental candidiasis, cryptococcosis and aspergillosis in mice. Chemotherapy. 1982;28(6):461–479. doi: 10.1159/000238138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vialaneix J. P., Chouini N., Malet-Martino M. C., Martino R., Michel G., Lepargneur J. P. Noninvasive and quantitative 19F nuclear magnetic resonance study of flucytosine metabolism in Candida strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):756–762. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G. E., Shadomy S. Studies on the mode of action of 5-fluorocytosine in Aspergillus species. Chemotherapy. 1979;25(2):61–69. doi: 10.1159/000237824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf A. R., Polak A. Mechanisms of action of 5-fluorocytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):79–85. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto A., Umezu K., Kobayashi K., Tomita K. Orotidylate decarboxylase (yeast). Methods Enzymol. 1978;51:74–79. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)51013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


