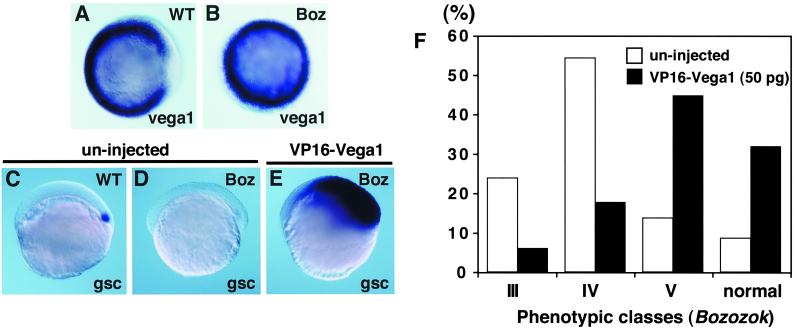
Figure 4.
VP16-vega1 can rescue both gsc expression and boz phenotype. Whole-mount in situ hybridization for vega1 (A and B, shield stage, animal view) and gsc (C–E, 40% epiboly stage, lateral view). Genotyping of boz mutants was carried out by restriction fragment polymorphism (11). (A) bozm168/+ phenotypically wild type. (B) bozm168/m168 mutant. (C) Uninjected wild-type embryo. (D) Uninjected bozm168/m168 embryo. Expression of gsc was suppressed in all uninjected boz embryos (n = 15). (E) VP16-vega1 mRNA (100pg) was injected into one-cell stage of embryos obtained from a bozm168/m168 × bozm168/m168 cross. Expansion of gsc was observed in all VP16-vega1-injected boz embryos (100%, n = 39). (F) Suppression of boz phenotype by VP16-vega1 injection. VP16-vega1 mRNA (50 pg) was injected into one-cell stage of embryos obtained from bozm168/m168 × bozm168/m168 crosses. The boz phenotype was classified by morphological criteria at 30 hpf as described previously (11). The number of uninjected and VP16-vega1-injected embryos was 59 and 85, respectively. Class V has a small break in trunk notochord with normal head structure; there is a two-to-several somite wide gap in the trunk notochord of class IV; class III shows partial cyclopia with anterior head deficiency and usually a large gap in the trunk notochord. Essentially identical results were obtained in several independent experiments.