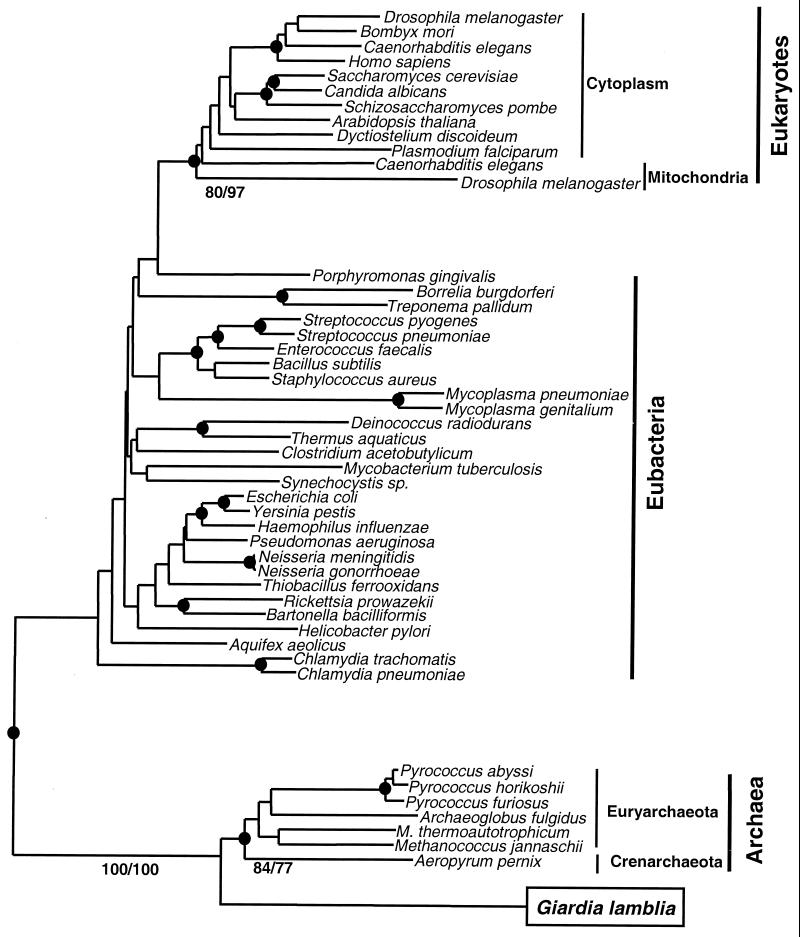
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of AlaRS sequences. Neighbor-joining (NJ) tree constructed by using the programs neighbor and protdist (24), where the number of amino acid substitutions per site in pairwise comparisons of aligned sequences (415 amino acids in length) were estimated by using the Dayhoff 120 matrix (22). The position of Giardia AlaRS is boxed. A similar tree topology was determined in 100 replicate random heuristic searches by using the maximum parsimony (MP) method (24) (one minimal length tree, 4821 steps long). ●, Those nodes supported in 70% or greater of 1,000 random bootstrap replicates of both MP and NJ trees. Bootstrap values for critical nodes are shown as % of 1,000 replicates in MP/NJ methods. The node leading to G. lamblia and archaeal species was consistently supported in 100% of replications. Furthermore, the shown tree topology was significantly better statistically [Kishino-Hasegawa and Templeton tests (25); P < 0.05] than all other alternative topologies of the major groups, including one where eukaryotes and G. lamblia were clustered together.