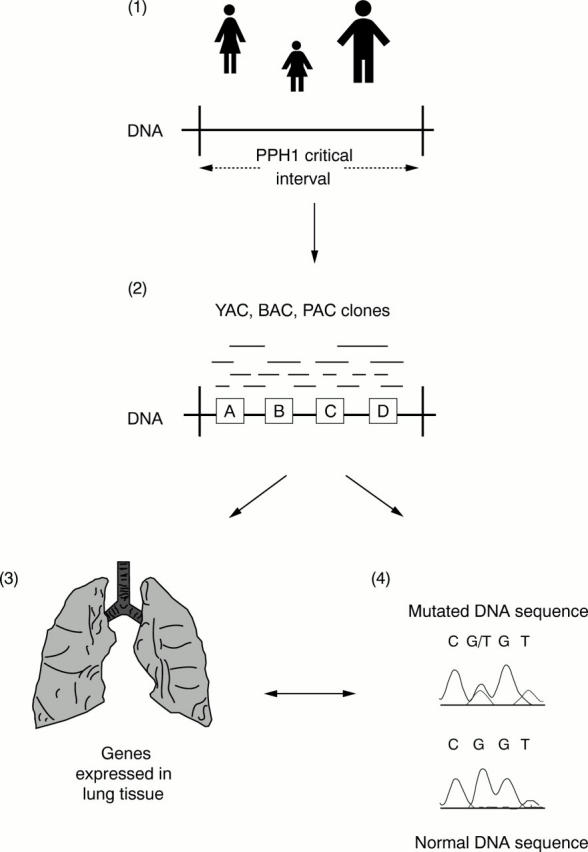
Figure 3 Idealised positional cloning strategy to identify the PPH1 gene. (1) First, further families with primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH) are required to reduce the PPH1 critical interval by the detection of recombinant events; that is, identifying that part of 2q33 shared by affected individuals within a family. (2) Use of data from the human genome project to identify genes and expressed sequence tags (ESTs or partially sequenced genes) that appear to be contained within the PPH1 critical interval (for example, genes A, B, C, and D). To place these genes, ESTs, and other DNA markers in the correct order, a series of overlapping DNA clones inserted into yeast, bacteria, or plasmid artificial chromosomes (YACs, BACs, and PACs, respectively) is created: a so called physical map. (3) Studies are undertaken to identify which of these genes are expressed in lung tissue and hence are good candidates for PPH1. (4) Finally, direct analysis of genes to detect a mutation in affected individuals compared with normal controls.
