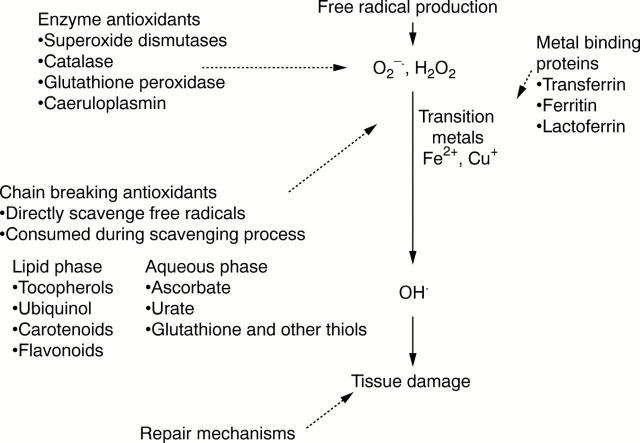
Figure 2 Antioxidant defences against free radical attack. Antioxidant enzymes catalyse the breakdown of free radical species, usually in the intracellular environment. Transition metal binding proteins prevent the interaction of transition metals such as iron and copper with hydrogen peroxide and superoxide producing highly reactive hydroxyl radicals. Chain breaking antioxidants are powerful electron donors and react preferentially with free radicals before important target molecules are damaged. In doing so, the antioxidant is oxidised and must be regenerated or replaced. By definition, the antioxidant radical is relatively unreactive and unable to attack further molecules.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.