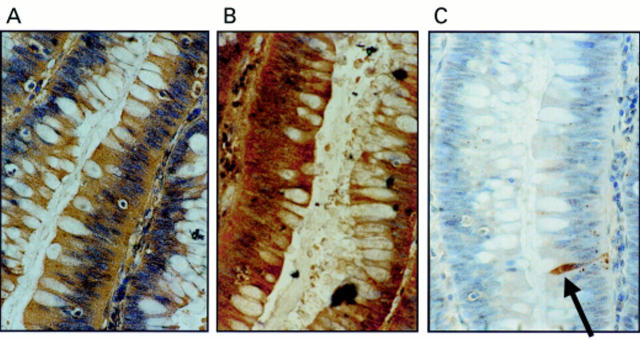
Figure 1 Coexpression of Fas ligand (FasL) and Fas in colonic adenomas is not associated with Fas mediated apoptosis. (A) Immunoperoxidase staining using a FasL specific rabbit polyclonal antibody was performed on paraffin wax embedded colonic adenoma sections. Slides were counterstained with haematoxylin. FasL positive immunohistochemical staining (brown) is shown in a representative mildly dysplastic villous adenoma. As a control for specificity of antibody detection, the FasL immunising peptide was included during primary antibody incubation. Competitive displacement of staining by the immunising peptide confirmed FasL specificity (not shown). (B) Another section sequential to that shown in (A) was used to detect Fas, using immunoperoxidase staining with a Fas specific rabbit polyclonal antibody. Fas positive immunohistochemical staining (brown) was present in the adenoma cells. (C) Cell death detection in situ by terminal transferase mediated dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL). Sections sequential to those shown in (A) and (B) were used to detect cell death by enzymic labelling of DNA strand breaks using TUNEL. Only those cells with positive TUNEL staining (brown) and exhibiting apoptotic morphology (arrow) were considered to be apoptotic. Only occasional TUNEL positive cells were identified despite widespread Fas–FasL coexpression. Control sections (not shown) where the terminal transferase was omitted were negative. These results are representative of 38 colonic adenomas.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.