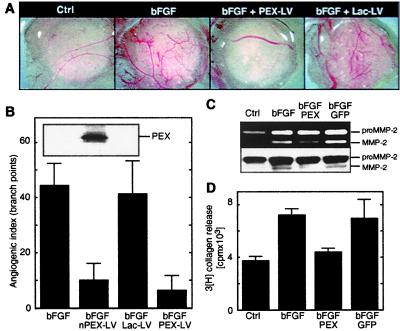
Figure 3.
Effects of PEX on angiogenesis in the chick CAM model. (A—D) Virally delivered PEX inhibits bFGF-induced angiogenesis through inhibition of MMP-2 activation. (A) Chick CAMs incubated for 72 h with filter disks soaked in PBS (Ctrl), bFGF, bFGF in the presence of PEX lentivirus (bFGF + PEX-LV), or LacZ virus (bFGF + Lac-LV). (B) Quantification of bFGF-induced angiogenic response by counting vessel branch points. (Inset) Western blot analysis using TV88 antibody to detect PEX expression in CAM lysates (from left to right: bFGF, bFGF + PEX-LV, bFGF + Lac-LV). (C and D) bFGF-induced MMP-2 activation (gelatin zymography) (C Upper) and collagenolytic (D) activity in CAM lysates. The same CAM lysates were used both for gelatin zymography and for collagenase assays. The upper and lower bands correspond to the 72-kDa MMP-2 proenzyme (proMMP-2) and the activated MMP-2 (≈62 kDa), respectively. To ensure the presence of the MMP-2 proenzyme in equal amounts, lysates also were analyzed by Western blotting (C Lower) by using MMP-2 specific mAb TV88. Ctrl, PBS-treated CAM; FGF, bFGF-treated CAM; bFGFPEX, PEX-expressing CAM treated with bFGF; bFGFGFP, GFP-expressing CAM treated with bFGF.