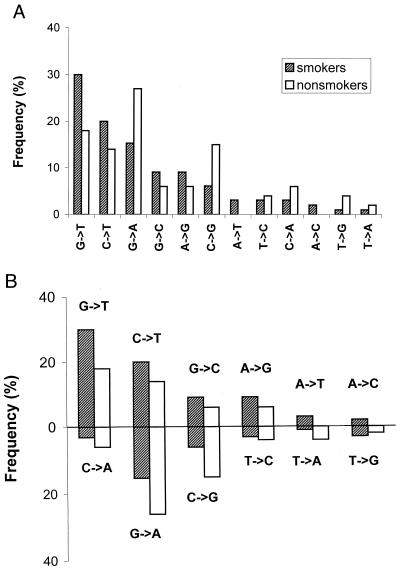
Figure 1.
p53 mutational patterns of lung adenocarcinomas from smokers (99 mutations) and nonsmokers (50 mutations). Because the strand with original lesions is identifiable only for (G→T, C→A), (G→C, C→G), and (C→T, G→A) pairs of complementary substitutions, we used only these three pairs to test the “mutagenesis” vs. “strand-asymmetric repair” alternative (see text). (A) In a standard (strand-nonspecific) representation, the patterns of smokers and nonsmokers show a difference, although statistically insignificant (P value 0.151). (B) The same patterns as in A, but organized as pairs of complementary transitions and transversions; the upper part may represent a nontranscribed strand, and the lower part, a transcribed strand.