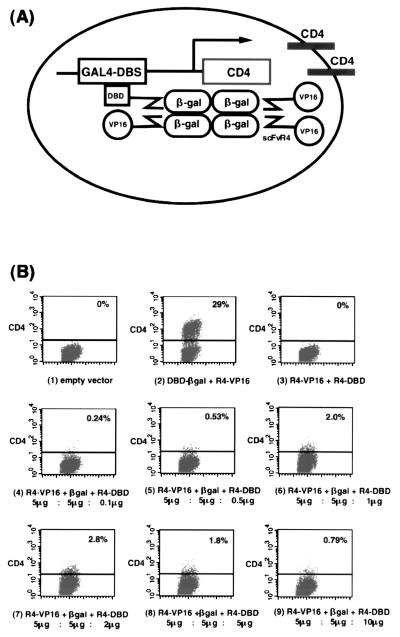
Figure 1.
Mammalian two-hybrid scFv-β-gal transcription assay. (A) Diagram depicting the effect of cotransfecting expression vectors encoding the anti-β-gal antibody fragment scFvR4-DBD fusion protein and scFvR4-VP16 (VP16 transcriptional transactivating domain) fusion proteins in the CHO-CD4 reporter cell line. The scFvR4-DBD and scFvR4-VP16 fusion proteins, when bound to a β-gal tetramer, can form a transcription complex that can bind to the chromosomal GAL4 DNA-binding site (DBS) and controls transcription of the CD4 reporter gene. (B) CHO-CD4 cells were cotransfected with β-gal expression clone pEF-βgal, together with various expression vectors. Induction of cell surface CD4 expression was assayed after 60 h by using anti-human CD4 antibody. The indicated percentage of CD4+ cells after 48 h was estimated with a FACSCalibur machine. The coexpressed vectors with pEF-βgal were as follows: 1, pEF-BOS vector only; 2, DBD-βgal and scFvR4-VP16; 3, scFvR4-VP16 and scFvR4-DBD; and 4–9, various amounts of scFvR4-VP16 and scFvR4-DBD as indicated. The amount of pEF-βgal plasmid (5 μg) was not varied.