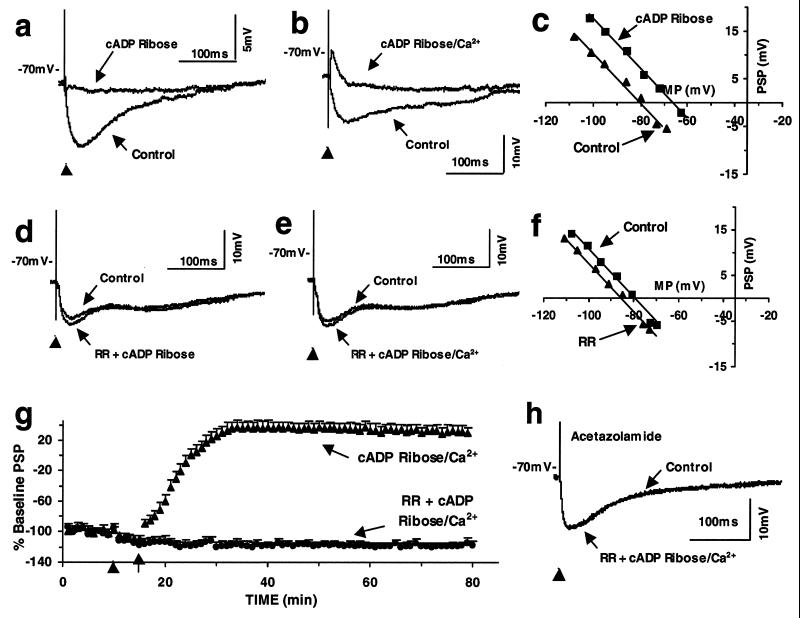
Figure 3.
(a–c) cADP-ribose reduces BAS-CA1 IPSP and reverses the IPSP to EPSP when associated with postsynaptic depolarization and shifts the potential response–membrane potential curve to the right. (d–f) RR prevents cADP-ribose- and cADP-ribose postsynaptic depolarization-induced changes in the BAS-CA1 responses and shifts the potential response–membrane potential curve to the left. (g) Time courses of the response to cADP-ribose postsynaptic depolarization (cADP-ribose/Ca2+; at arrow) as compared with those of pre-RR application (at arrowhead); each point represents the mean PSP magnitudes + SEM normalized to the average of their control values before application of agents. In the cADP-ribose/Ca2+ group, the same procedure (sham injection of RR at arrowhead) also was applied through the electrode containing no RR. (h) Acetazolamide (1 μM, 30 min) prevents cADP-ribose postsynaptic depolarization-induced changes in the BAS-CA1 responses (40 min after cADP-ribose postsynaptic depolarization vs. control trace).