Figure 1.
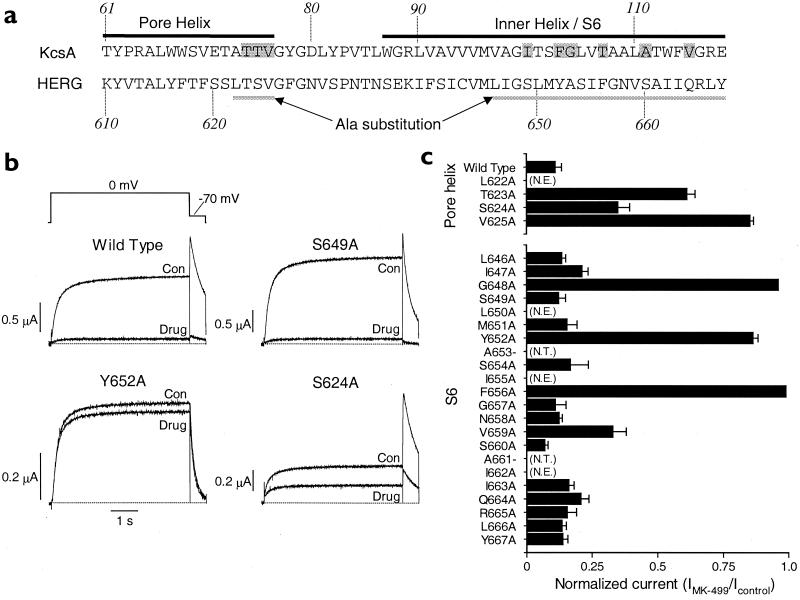
Alanine-scanning mutagenesis of HERG to define binding sites for MK-499. (a) Sequence of the pore helix and inner helix for the KcsA channel (19) and the equivalent residues in the pore helix and S6 transmembrane domain of the HERG K+ channel. Shaded residues of KcsA face the inside of the inner channel pore. The region of HERG analyzed by Ala-scanning mutagenesis is underlined. (b) Block of WT and mutant HERG channel current in oocytes by MK-499. HERG channel currents recorded before (Con) and after (Drug) achieving steady-state block of current with 0.3 μM MK-499. Currents were elicited during 5-s pulses to 0 mV from a holding potential of −90 mV, applied repetitively at 0.166 Hz. (c) Normalized current (IMK499/Icontrol) measured after steady-state block by 0.3 μM MK-499 (n = 4–6; error bars, ±SEM). A value of 1 indicates no detectable decrease in current by the drug. N.T., residues that were not tested; N.E., mutant channels that lacked functional expression.