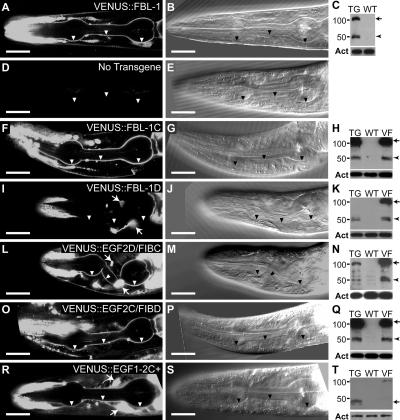
Figure 5.
EGF2C and FIBC domains are redundant signals for localization to pharyngeal basal lamina. (left and middle) Heads of fbl-1(q771) L4 larvae; transgenes are noted in the figure. Arrowheads indicate pharyngeal basal lamina; anterior to the left. Arrows indicate fluorescence from the coinjection marker. Bars, 20 μm. (left) 0.8-μm confocal slices. (middle) Differential interference contrast image of the same animal. (A, F, L, O, and R) Constructs with either EGF2C or FIBC localize to pharyngeal basal lamina. (I) VENUS∷FBL-1D not in pharyngeal basal lamina. (right) Anti-VENUS Western blots. Both full-length FBL-1 isoforms are predicted to migrate at ∼100 kD, but FBL-1D only accumulates an ∼50-kD degradation product. TG, extract from transgenic strain noted in the left column; WT, extract from wild-type animals not carrying transgene; VF, extract from animals carrying VENUS∷FBL-1; Act, actin loading control. Arrows mark the predicted sizes of transgenic proteins. Arrowheads mark abundant degradation products.