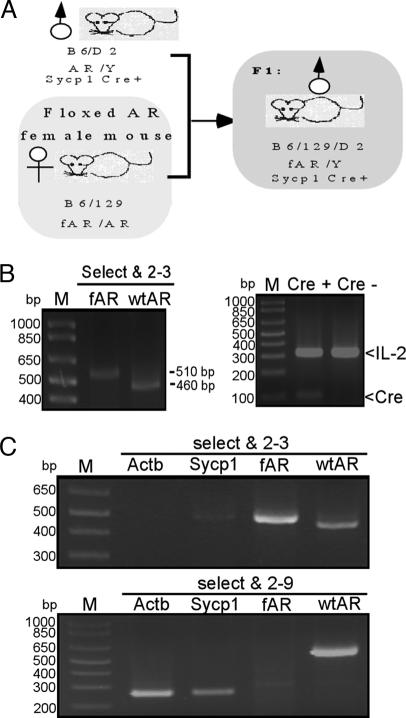
Fig. 1.
Generation and genotyping of germ cell-specific AR knockout (G-AR−/y) mice. (A) Mating strategy and study design. The mouse marked by the gray box is a Sycp1-Cre conditional AR knockout male (G-AR−/y) mouse. (B) Genotyping of tail genomic DNA of G-AR−/y mice. The WT allele of the AR gene generated a PCR product ≈460 bp in size by primers “select and 2–3.” The fAR gene generated a ≈510-bp product with the same primers. The presence of the Sycp1-Cre and internal control IL-2 genes was confirmed by PCR. (C) (Upper) Genotyping of testis genomic DNA of G-AR−/y mice using primers “select and 2–3.” The PCR product amplified by “select and 2–3” can distinguish WT and fAR alleles with PCR products ≈460 and ≈510 bp, respectively. (Lower) Genotyping of testis genomic DNA of G-AR−/y mice using primers “select and 2–9.” The WT allele generated a ≈600-bp product. fAR with neo cassette was too large to get a PCR product under these conditions. With the fAR recombined by Sycp1-Cre, the recombinant allele produced a ≈270-bp product using the same primers.