Fig. 3.
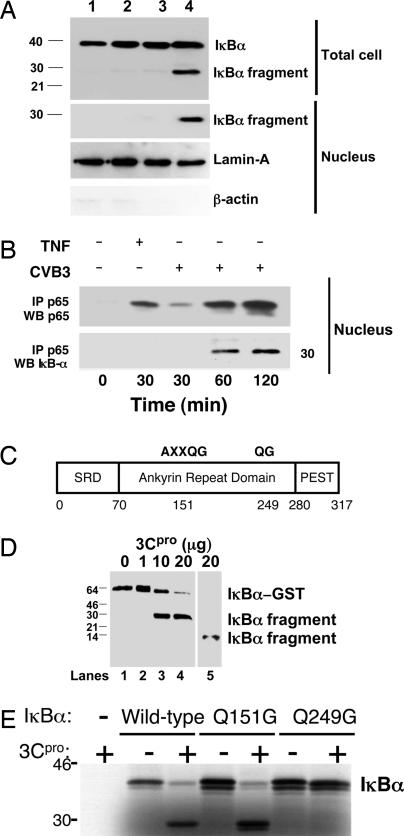
The CVB3 viral protease 3Cpro cleaves IκBα. (A) HeLa cells were treated with media alone (lane 1) or CVB3 for 15 min (lane 2), 30 min (lane 3), or 120 min (lane 4). Total cell lysates (Upper) and nuclear extracts (Lower) were immunoblotted with antibody to IκBα, lamin-A, and β-actin. An IκBα fragment is present in infected cells. (B) HeLa cells were infected with CVB3 for 0–2 h or treated with TNF-α for 30 min, and nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated with antibody to p65 and immunoblotted with antibody to p65 (Upper) or antibody to the N terminus of IκBα (Lower). CVB3 infection leads to the appearance of an NF-κB:IκBα complex in the nucleus. (C) Schematic of the primary structure of IκBα with potential consensus 3Cpro cleavage sites at amino acid residues 151–155 and 249–250. Q is the P1 residue and G is the P1′ residue of the consensus cleavage sites. SRD is the signal receiving domain. PEST is a domain rich in proline, glutamate, serine, and threonine residues. (D) 3Cpro cleaves IκBα in vitro. Recombinant GST- IκBα was incubated with recombinant (His)6-3Cpro, fractionated by SDS/PAGE, and immunoblotted with antibody to the N terminus of IκBα (lanes 2–4) or antibody to the C terminus of IκBα (lane 5). (E) 3Cpro cleavage of IκBα mutants in vitro. WT or mutant 35S-labeled recombinant IκBα was incubated with recombinant 3Cpro, fractionated by SDS/PAGE, and autoradiographed. 3Cpro cleaves IκBα(WT) and IκBα(Q154G) but not IκBα(Q249G).