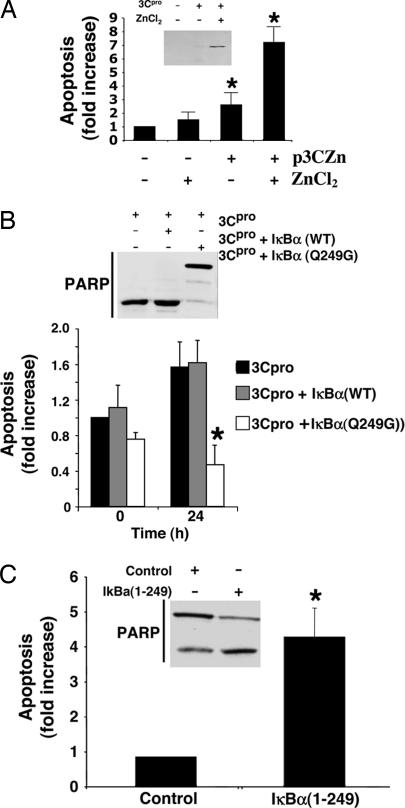
Fig. 5.
Viral protease generates an IκBα fragment that causes apoptosis. (A) 3Cpro induces apoptosis in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the pZn3Cpro vector, which encodes 3Cpro regulated by a Zn-responsive promoter element. ZnCl2 treatment induces 3Cpro expression (Inset). HeLa cells transfected with pZn3Cpro and treated with ZnCl2 were assayed for apoptosis. Expression of the 3Cpro protease causes apoptosis (n = 3 ± SD; ∗, P < 0.05). (B) Cleavage-resistant IκBα(Q249G) inhibits protease-induced apoptosis. HeLa cell lines expressing WT IκBα or mutant IκBα(Q249G) were transiently transfected with pZn3Cpro, treated with ZnCl2 for 0 or 24 h, and assayed for apoptosis by FACS [n = 3 ± SD; ∗, P < 0.05 vs. IκBα(WT)], and by PARP cleavage (Inset). (C) The IκBα fragment activates apoptosis. HeLa cells were transfected with an empty control vector or a vector expressing the IκBα fragment. Transfected cells were stimulated with TNF-α for 30 min and then apoptosis was measured by FACS and PARP cleavage (Inset). n = 3 ± SD; ∗, P < 0.05.