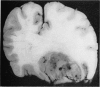
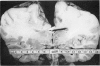
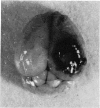
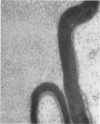
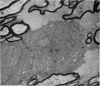
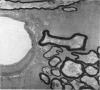
Full text
PDF































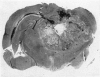
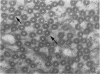
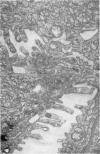
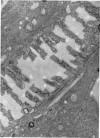
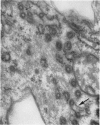
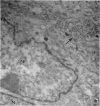
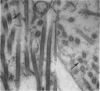
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleu F. P., Katzman R., Terry R. D. Fine structure and electrolyte analyses of cerebral edema induced by alkyl tin intoxication. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Jul;22(3):403–413. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196307000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHARD W. The detection and study of tumor viruses with the electron microscope. Cancer Res. 1960 Jun;20:712–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., GERSCHENFELD H. M., WALD F. Cellular mechanism of myelination in the central nervous system. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Sep 25;4(5):651–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.5.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., HARTMANN J. F. Neuroglial structure and relationships as revealed by electron microscopy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1957 Jan;16(1):18–39. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195701000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GONATAS N. K., ZIMMERMAN H. M., LEVINE S. Ultrastructure of inflammation with edema in the rat brain. Am J Pathol. 1963 Apr;42:455–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., ZIMMERMAN H. M., LEVINE S. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF CEREBRAL FLUID ACCUMULATION. III. EXTRACELLULAR SPREAD OF CRYPTOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDES IN THE ACUTE STAGE. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jul;45:1–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., ZIMMERMAN H. M., LEVINE S. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF CEREBRAL FLUID ACCUMULATION. IV. ON THE NATURE AND ORIGIN OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUIDS FOLLOWING CRYPTOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE IMPLANTATION. Am J Pathol. 1964 Aug;45:195–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZMAN R., GONATAS N., LEVINE S. ELECTROLYTES AND FLUIDS IN EXPERIMENTAL FOCAL LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY. Arch Neurol. 1964 Jan;10:58–65. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460130062009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLATZO I., PIRAUX A., LASKOWSKI E. J. The relationship between edema, blood-brain-barrier and tissue elements in a local brain injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1958 Oct;17(4):548–564. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195810000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., ZIMMERMAN H. M., WENK E. J., GONATAS N. K. Experimental leukoencephalopathies due to implantation of foreign substances. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jan;42:97–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUSE S. A. Electron microscopic observations of the central nervous system. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Sep 25;2(5):531–542. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUSE S. A., HARRIS B. Electron microscopy of the brain in experimental edema. J Neurosurg. 1960 May;17:439–446. doi: 10.3171/jns.1960.17.3.0439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYNARD E. A., SCHULTZ R. L., PEASE D. C. Electron microscopy of the vascular bed of rat cerebral cortex. Am J Anat. 1957 May;100(3):409–433. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001000306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ R. L., MAYNARD E. A., PEASE D. C. Electron microscopy of neurons and neuroglia of cerebral cortex and corpus callosum. Am J Anat. 1957 May;100(3):369–407. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORACK R. M., TERRY R. D., ZIMMERMAN H. M. The fine structure of cerebral fluid accumulation. I. Swelling secondary to cold injury. Am J Pathol. 1959 Nov-Dec;35:1135–1147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORACK R. M., TERRY R. D., ZIMMERMAN H. M. The fine structure of cerebral fluid accumulation. II. Swelling produced by triethyl tin poisoning and its comparison with that in the human brain. Am J Pathol. 1960 Mar;36:273–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]