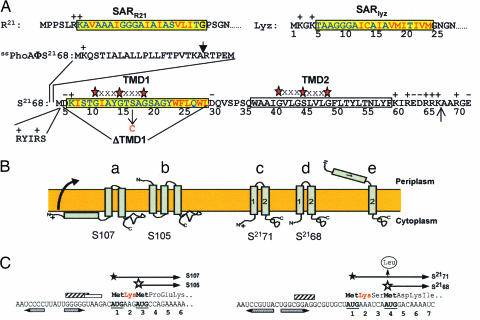
Fig. 1.
Properties of holins and holin genes. (A) Primary structure of S2168 and the N-terminal domains of Lyz, R21, and PhoA. The codon numbering for S2168 follows that of the full-length gene product, S2171 (see C for the dual-start structure at the beginning of S21). The SAR sequences of Lyz and R21 (7, 8) and TMD1 of S2168 (16) are shown in the yellow boxes, with the residues that are polar or neutral in terms of hydrophobicity in blue and the hydrophobic residues in red. TMD2 of S2168 is shown in an uncolored box. The red stars separated by three Xs above the TMDs of S21 indicate GxxxG-like motifs that may mediate interhelical interactions (19). The vertical arrow above the PhoA sequence indicates the normal signal sequence cleavage site (27). In ssPhoAΦS2168, the indicated sequence from PhoA is fused to the Met4 codon of S21. The position of the S16C missense change is indicated by a vertical arrow below the TMD1 sequence. The N terminus of S2168 was given two additional positive charges by inserting the sequence RYIRS between positions 4 and 5. To generate S2168ΔTMD1, the indicated sequence was deleted from S2168. The vertical arrow between residues 66 and 67 indicates the position where the sequence G2H6G2 was inserted in the allele used for purification. (B) Holin topologies. The topologies of the λ antiholin, S107 (a), and holin, S105 (b), are shown (6, 13, 23, 28). (c) and (d) show S2171 and S2168 with two TMDs, respectively. In (e), the lethal form of S21 is shown with its TMD1 in the periplasm. (C) Translational control region of the λ and 21 holin genes (11, 15, 16). Filled and empty stars show starts of the long (antiholin) and short (holin) gene products. Shine-Dalgarno sequences for the first and second translational starts of Sλ are indicated by striped and empty boxes, respectively. The single Shine–Dalgarno sequence of S21 is indicated by a striped box. The horizontal inverted pairs of arrows show the RNA stem loops controlling the dual starts. For S21, the vertical arrow shows the Met-4 → Leu mutation, which eliminates the production of the holin from the allele referred to as S2171. The Lys residues conferring antiholin character to the longer translational product in both the S and S21 genes are shown in red.