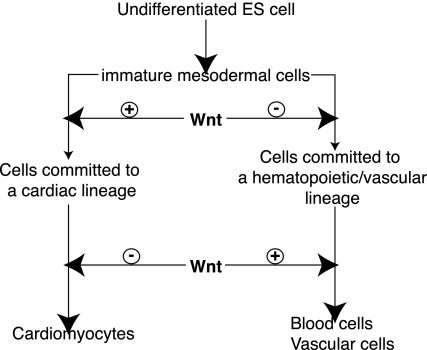
Fig. 5.
Wnt signals exhibit developmental stage-specific, biphasic, and antagonistic effects on cardiogenesis and hematopoiesis. In the early stage of development, Wnt signals promote cardiogenesis and inhibit hematopoiesis, whereas in the late stage of development, Wnt signals inhibit cardiomyocyte differentiation and promote blood cell differentiation.