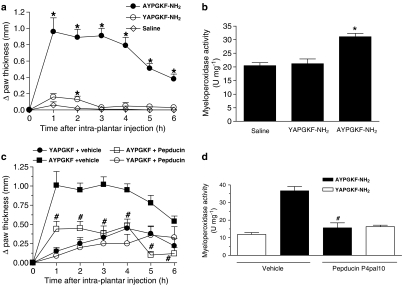
Figure 2.
Direct inflammatory effects of PAR4 activation in the mouse paw. The oedema formation (a) and granulocyte recruitment (b) were evaluated following an intraplantar injection of the PAR4-AP, AYPGKF-NH2 (50 μg), the control inactive peptide, YAPGKF-NH2 (50 μg), or the saline vehicle. The effect of a pepducin P4pal10 (0.25 mg kg−1) pretreatment was also evaluated against the oedema formation (c) and granulocyte recruitment (d) induced by AYPGKF-NH2 (50 μg) and YAPGKF-NH2 (50 μg). Values are mean±s.e.m. of n=5–8 per group. *Significantly different from the saline vehicle or the control peptide group (a and b), P<0.05; #significantly different from the vehicle+AYPGKF-NH2 group (c and d), P<0.05.