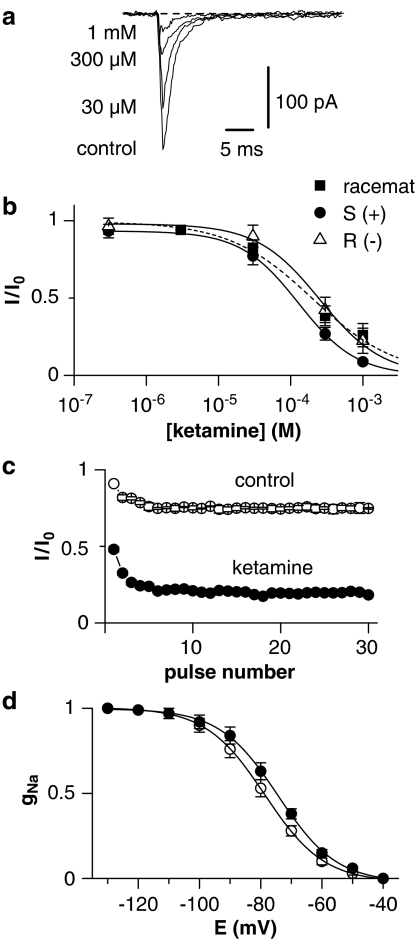
Figure 2.
Tonic and phasic blockade of Na+ current by ketamine in somata. (a) Recordings of Na+ current in the control solution and in the presence of 100, 300, and 1000 μM ketamine. Holding potential was set to −80 mV and Na+ currents were activated by 50-ms voltage steps to −20 mV after a 50-ms prepulse to −120 mV. (b) Concentration dependence of the Na+ current suppression by ketamine and its enantiomers (8 somata). The data points were fitted using equation (1). IC50 values are given in Table 1. Error bars indicate s.e. if exceeding symbol size. (c) Normalized amplitudes of Na+ currents recorded in control solution and in the presence of 100 μM ketamine as a function of pulse number. The currents were activated by a 10-ms voltage step to −20 mV at a frequency of 10 Hz. Holding potential was −80 mV. Each current was normalized to the amplitude of the first Na+ current recorded in control solution (10 somata). (d) Effects of ketamine on Na+ currents assessed by shifts in the steady-state availability curve. Each symbol represents the mean normalized fractional current derived from at least five different experiments. The data points were fitted by equation (2).