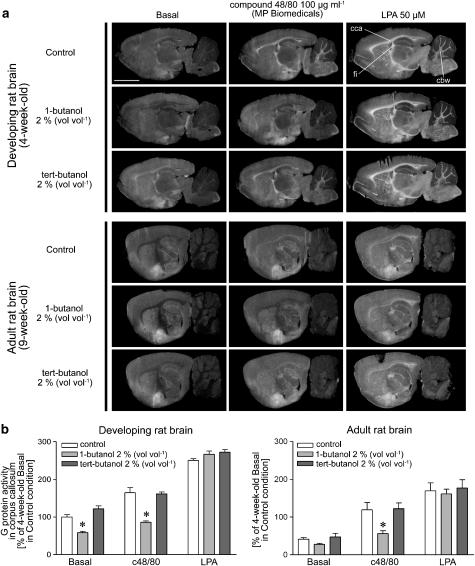
Figure 2.
c48/80 stimulates G protein activity in the developing white matter tracts through 1-butanol-sensitive mechanisms likely involving PLD. (a) [35S]GTPγS autoradiography of developing (4-week-old) and adult (9-week-old) rat brain sections was conducted using a three-step protocol with DPCPX (1 μM) present throughout steps 2 and 3, as detailed in the Methods section. c48/80 (100 μg ml−1; MP Biomedicals) or LPA (50 μM in 0.1% fatty acid-free BSA) and the structural butanol isomers (2%, vol vol−1) were present during the [35S]GTPγS labeling step, as indicated. Note that the PLD inhibitor 1-butanol but not its inactive isomer tert-butanol selectively inhibits c48/80-stimulated G protein activity in the developing white matter tracts without affecting LPA-evoked responses. Note also age-dependent decline in basal and c48/80- or LPA-evoked [35S]GTPγS binding responses throughout the adult white matter tracts. Abbreviations: cca, corpus callosum; fi; the fimbria of the hippocampus; cbw, the cerebellar white matter (cbw). Scale bar=5 mm. (b) Quantitative autoradiography data on the corpus callosum of 4-week-old (left) and 9-week-old rats (right). Autoradiography images were digitized and bound radioactivity values were obtained from the digitized images, as detailed in the Methods section. Values are mean+s.e.m. representing four sections from four (developing) or two (adult) individual animals. Risk level: *P<0.05 compared to the respective control treatment in the corpus callosum of 4-week-old rat (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison).