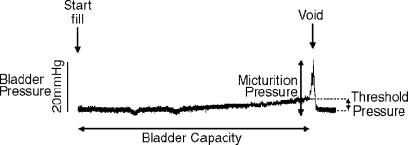
Figure 1.
An example trace of normal bladder cystometry in a urethane-anaesthetised guinea-pig. As saline is infused into the empty bladder (Start Fill) at a constant rate, bladder pressure initially remains low; however, as bladder volume increases, a slow rise in intravesical pressure is evident. Bladder filling continues until a threshold volume (which is equivalent to the bladder capacity) and threshold pressure (equivalent to the difference in pressure between that at the initiation of filling (baseline pressure) and that measured immediately prior to the initiation of the voiding response) are reached to initiate micturition. At this time, urethral pressure decreases and bladder pressure increases (micturition pressure) in order to allow expulsion of bladder contents.