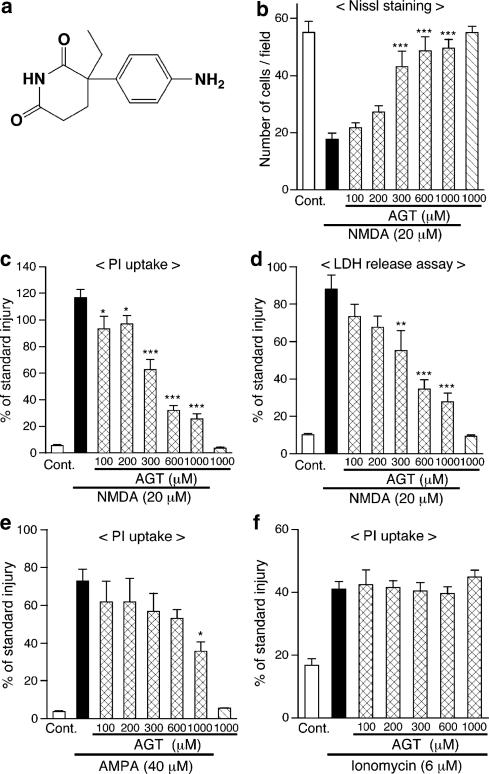
Figure 1.
Continuous application of aminoglutethimide (AGT) protects neurons in cerebrocortical slice cultures from cytotoxicity of NMDA and AMPA. (a) Chemical structure of AGT. (b–d) AGT was applied to slice cultures at indicated concentrations from 1 DIV, throughout the entire period of cultivation. NMDA (20 μM) was applied for 24 h at 11 DIV in the presence of AGT, and cellular injury at 12 DIV was determined by the number of Nissl-stained surviving neurons (b, n=6–7 slices), intensity of PI fluorescence (c, n=5–7 slices) and amount of LDH released into medium (d, n=4 culture wells). ‘Cont.' means control cultures that did not receive drug treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs NMDA alone. (e) AGT was applied to slice cultures at indicated concentrations from 1 DIV. AMPA (40 μM) was applied for 24 h at 11 DIV in the presence of AGT, and cellular injury at 12 DIV was determined by intensity of PI fluorescence (n=4–6 slices). *P<0.05 vs AMPA alone. (f) AGT was applied at indicated concentrations from 1 DIV, and ionomycin (6 μM) was applied for 24 h at 11 DIV in the presence of AGT. Cellular injury at 12 DIV was determined by PI fluorescence (n=5–6 slices). In (c–f), each value was normalized with that in slice cultures receiving the standard injury (200 μM NMDA for 24 h) as 100%.